Description
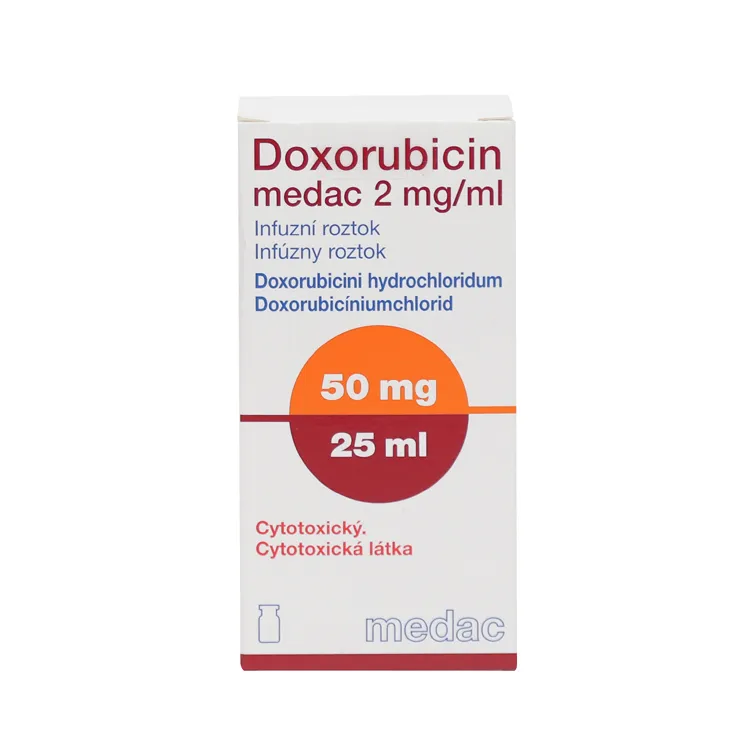
Doxorubicin (Doxorubicin) Solution for Infusions 2 mg/ml – 25 ml (50 mg) – Vial #1
Composition:
Each milliliter contains 2 mg of Doxorubicin hydrochloride.
Mechanism of Action:
Doxorubicin, a potent anthracycline antibiotic, exerts its antitumor effects by intercalating into DNA strands and inhibiting topoisomerase II. This mechanism leads to DNA damage and apoptosis in cancer cells.
Pharmacological Properties:
Doxorubicin is a cytotoxic agent that disrupts the growth of cancer cells by interfering with their DNA replication process.
Indications for Use:
Doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of various cancers, including breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, and soft tissue sarcomas.
Contraindications:
Contraindications include severe myelosuppression, severe hepatic impairment, and hypersensitivity to Doxorubicin or any of its components.
Side Effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Hair loss
- Myelosuppression
Usage Instructions:
Doxorubicin is administered intravenously by a healthcare professional in a clinical setting. Dosage is individualized based on factors such as body surface area and overall health.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Doxorubicin has shown significant efficacy in various cancers, leading to tumor regression and improved survival rates in patients compared to other chemotherapy agents.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Doxorubicin can be used in adult patients for the treatment of specified cancers. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for pediatric or elderly patients.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Store Doxorubicin vials in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture. The shelf life of the product should be checked and adhered to for optimal effectiveness.
Packaging Description:
The product is supplied in a vial containing 25 ml of the solution, equivalent to 50 mg of Doxorubicin hydrochloride.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Studies have shown the effectiveness of Doxorubicin in treating various cancers. For example, a study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology demonstrated high response rates and improved survival in advanced breast cancer patients treated with Doxorubicin-based regimens.