Description
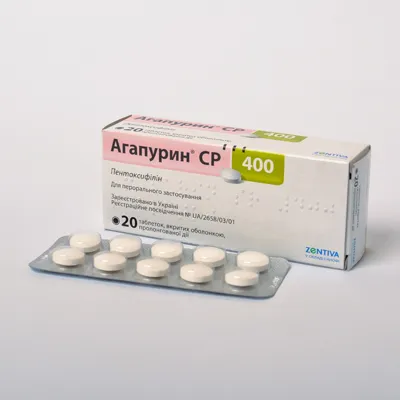
Agapurin SR (Pentoxifyllin) Coated Tablets with Prolonged Release 400 mg. №20
Ingredients:
- Each coated tablet contains 400 mg of pentoxifylline.
Dosage:
- The usual dose is one tablet twice a day, preferably with meals.
Indications:
- Agapurin SR is indicated for the treatment of peripheral vascular diseases.
- It helps improve blood flow and reduces the viscosity of blood, which can benefit individuals with circulation issues.
Contraindications:
- Do not use Agapurin SR if you have a history of bleeding disorders or recent hemorrhage.
- It is also contraindicated in patients with acute myocardial infarction and those prone to allergic reactions to the drug.
Directions:
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet.
- Follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Scientific Evidence:
- Pentoxifylline, the active ingredient in Agapurin SR, has been extensively studied for its effects on peripheral vascular diseases.
- Research published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery demonstrated that pentoxifylline can improve symptoms and increase walking distance in patients with intermittent claudication.
- A meta-analysis published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews supported the use of pentoxifylline for improving blood flow and symptoms in individuals with peripheral artery disease.
Additional Information:
- Agapurin SR with prolonged release offers a convenient dosing regimen for individuals requiring long-term management of peripheral vascular diseases.
- It is important to adhere to the prescribed dosage and consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
- If you experience any adverse effects or have concerns about the medication, seek medical advice promptly.
Pharmacological Effects: Pentoxifylline works by improving blood flow through its vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps reduce blood viscosity and enhance red blood cell flexibility, leading to improved circulation in the peripheral vessels.
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials have shown that Agapurin SR can effectively improve symptoms such as leg pain and cramping associated with peripheral vascular diseases. A study published in the European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery reported significant improvements in walking distance and quality of life in patients treated with pentoxifylline compared to a control group.