Description
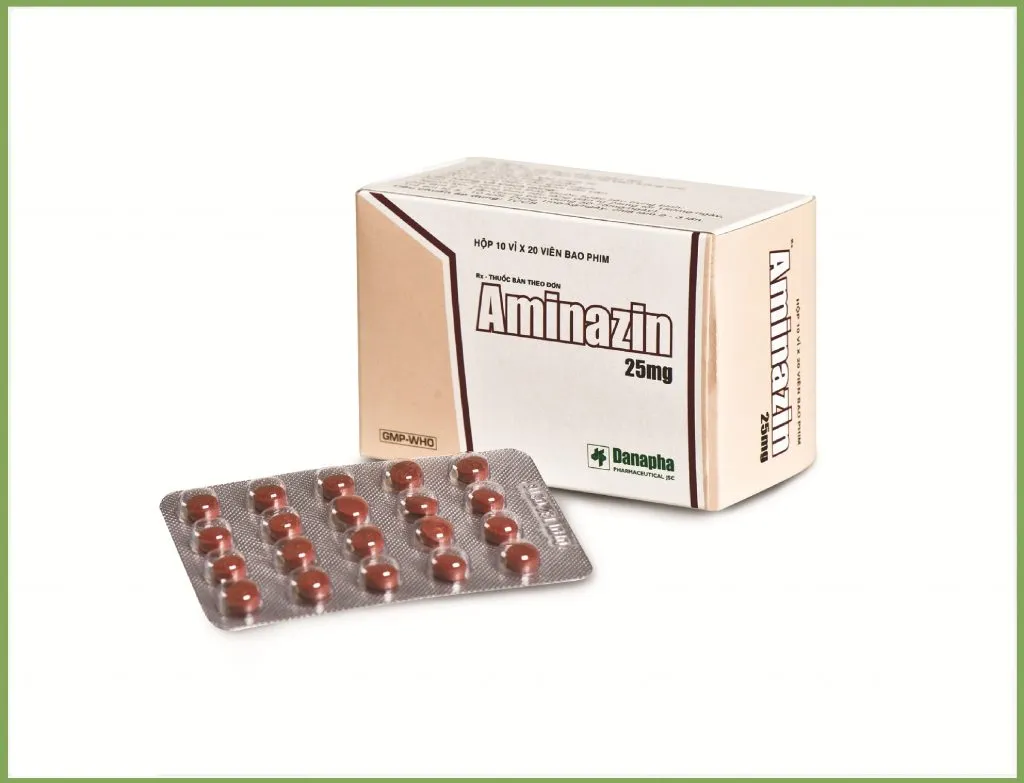
Aminazin (Chlorpromazine) Coated Tablets 25 mg. №20
Ingredients:
Each coated tablet contains 25 mg of Chlorpromazine as the active ingredient.
Dosage:
The usual adult dose is 25-50 mg three times daily. Dosage may vary based on the condition being treated.
Indications:
Aminazin tablets are indicated for the management of various psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia and manic-depressive illness.
Contraindications:
Do not use Aminazin tablets in patients with known hypersensitivity to Chlorpromazine or other phenothiazines.
Directions:
Swallow the tablets whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablets.
Scientific Evidence:
Chlorpromazine, the active ingredient in Aminazin tablets, exerts its antipsychotic effects by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. This action helps alleviate symptoms of psychosis such as hallucinations and delusions. Studies have shown that Chlorpromazine is effective in managing acute psychotic episodes and preventing their recurrence.
Research published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology demonstrated the efficacy of Chlorpromazine in treating schizophrenia, with significant improvements in positive symptoms and overall functioning observed in patients. The drug’s long-standing presence in clinical practice further supports its effectiveness in managing various psychiatric conditions.
Additional Information:
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Aminazin tablets should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as the drug may pass into breast milk and affect the infant.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of Aminazin tablets include drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation. Contact your healthcare provider if these side effects persist or worsen.