Description
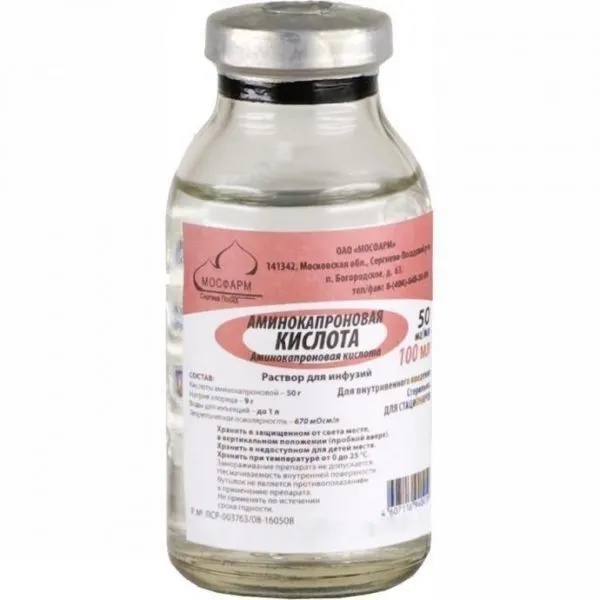
Aminocaproic Acid (Aminocaproic Acid) 5% 100 ml
Ingredients:
Aminocaproic acid (aminocaproic acid) 5% solution in a 100 ml bottle.
Mechanism of Action:
Aminocaproic acid functions as an antifibrinolytic agent by inhibiting the activation of plasminogen to plasmin, thereby preventing the breakdown of blood clots and reducing excessive bleeding.
Pharmacological Properties:
Aminocaproic acid exerts its hemostatic effect by stabilizing blood clots and promoting coagulation, leading to decreased bleeding tendencies.
Indications for Use:
- Treatment of excessive bleeding during surgical procedures
- Management of bleeding resulting from trauma
- Control of hemorrhage in patients with underlying medical conditions affecting coagulation
Contraindications:
Aminocaproic acid should not be administered to individuals with a known hypersensitivity to the drug. Caution is advised in patients with a history of thromboembolic diseases.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of aminocaproic acid may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and muscle pain. Serious adverse reactions such as thrombosis or allergic reactions are rare but should be monitored for.
Usage Instructions:
For adults, the typical dosage of aminocaproic acid is 4 to 5 grams (80-100 mL) every 6 hours, with adjustments based on individual patient needs. Administration is usually via intravenous route under medical supervision.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Aminocaproic acid has demonstrated comparable efficacy to tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss during cardiac surgeries, highlighting its effectiveness as a hemostatic agent in various clinical settings.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Aminocaproic acid can be safely used in adult populations, including the elderly, for managing bleeding episodes associated with surgical interventions or trauma.
Storage Conditions and Shelf Life:
Store aminocaproic acid at room temperature away from moisture and heat. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use the product beyond the indicated shelf life.
Packaging Description:
The product is supplied in a 100 ml bottle containing a 5% solution of aminocaproic acid, clearly labeled with dosage information and handling instructions.
Scientific Evidence:
Aminocaproic acid’s efficacy in reducing blood loss during surgeries and managing bleeding disorders has been supported by clinical studies. Notably, a comparative study published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis demonstrated its effectiveness similar to tranexamic acid in cardiac surgery settings.