Description
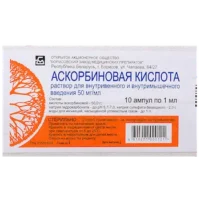
Ascorbic Acid (Ascorbic Acid) Ampoules 10% 2 ml. №10
Ingredients:
Each ampoule contains 10% Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C).
Mechanism of Action:
Ascorbic Acid acts as a co-factor for enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of collagen, carnitine, and neurotransmitters. It also functions as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Pharmacological Properties:
Ascorbic Acid is essential for the biosynthesis of collagen, an important structural protein in connective tissues. It enhances iron absorption in the gut and plays a crucial role in immune function by supporting various cellular functions.
Indications for Use:
Ascorbic Acid ampoules are indicated for the treatment and prevention of Vitamin C deficiency. They are essential for collagen synthesis, wound healing, and immune function maintenance.
Contraindications:
Do not use Ascorbic Acid ampoules if you have a known allergy to Vitamin C or any of the ingredients. Consult a healthcare provider before use if pregnant, nursing, or have any medical conditions that may interact with Vitamin C supplementation.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of Ascorbic Acid may include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. In rare cases, allergic reactions like rash or itching may occur.
Usage Instructions:
Administer the ampoules as directed by a healthcare professional. The typical route of administration is via intramuscular or intravenous injection. Strict adherence to aseptic techniques during administration is crucial.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Ascorbic Acid ampoules offer a reliable and efficient method of delivering Vitamin C, ensuring rapid absorption and utilization by the body. Compared to oral supplements, parenteral administration bypasses the digestive system, making it ideal for individuals with malabsorption issues.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Ascorbic Acid ampoules are suitable for a wide range of patient groups, including children, adults, and the elderly. However, special caution should be exercised in patients with renal impairment or a history of kidney stones.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Store Ascorbic Acid ampoules in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Do not freeze. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use the product beyond the stated shelf life.
Packaging Description:
The product is available in boxes containing 10 ampoules, each with a volume of 2 ml. The ampoules are made of clear glass and are sealed to ensure product integrity.
Scientific Evidence:
Ascorbic Acid has been extensively studied, with research demonstrating its role in immune modulation, antioxidant defense, and skin health. Clinical studies have shown that Vitamin C supplementation can reduce the risk of developing common colds and improve wound healing outcomes.