Description
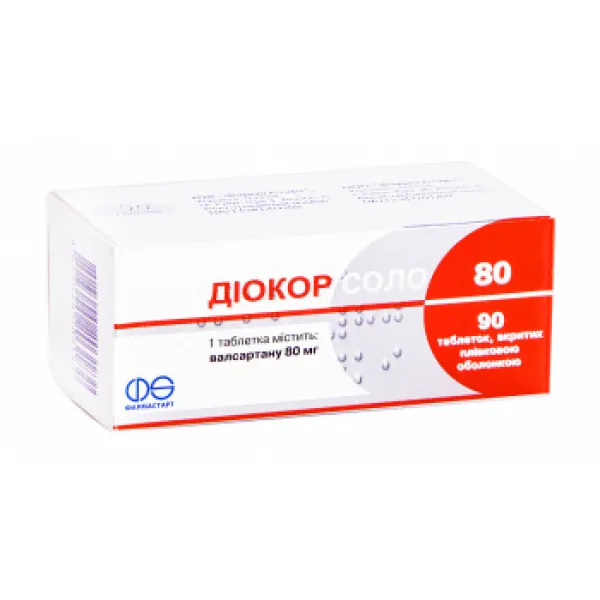
Diocor 80 (Valsartan, Hydrochlorothiazide) Coated Tablets 80 mg/12.5 mg. №90
Ingredients
Diocor 80 tablets contain 80 mg of valsartan and 12.5 mg of hydrochlorothiazide. Valsartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), while hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. These two components work together to lower blood pressure by different mechanisms of action.
Dosage
The recommended dosage of Diocor 80 is one tablet once daily. It is important to follow the prescribed regimen provided by your healthcare provider. Do not exceed the recommended dose unless directed by a physician.
Indications
Diocor 80 tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension in patients who require initial therapy or as a substitute for monotherapy. It is effective in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Contraindications
Do not use Diocor 80 if you are allergic to any of the ingredients, if you are pregnant, or if you have severe renal impairment. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting this medication to ensure it is safe for you.
Directions
Take Diocor 80 tablets orally with or without food, as directed by your doctor. Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
Scientific Evidence
Studies have shown that the combination of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in Diocor 80 tablets is effective in lowering blood pressure. Research published in the Journal of Clinical Hypertension demonstrated the superior efficacy of this combination therapy compared to monotherapy in patients with hypertension.
Additional Information
It is important to monitor your blood pressure regularly while taking Diocor 80 tablets. Inform your healthcare provider of any side effects or concerns. This medication may cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially during the first few days of treatment. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how this medication affects you.
Pharmacological Effects: Valsartan works by blocking the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that constricts blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure. Hydrochlorothiazide acts on the kidneys to increase the excretion of sodium and water, further lowering blood pressure.
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of Diocor 80 tablets in the management of hypertension. A randomized controlled trial published in the American Journal of Medicine showed a significant reduction in blood pressure levels with the use of valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy.