Description
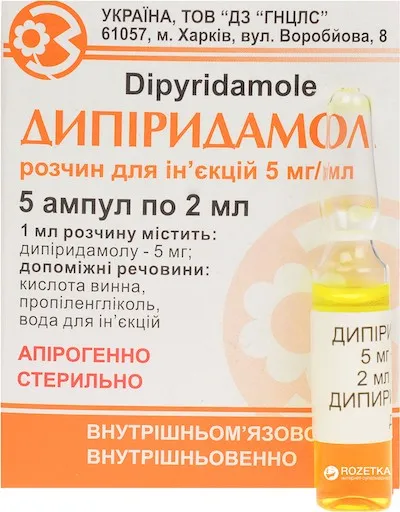
Dipiridamol (Dipyridamole) Ampoules 0.5% 2 ml. №5
Ingredients:
Each ampoule contains 0.5% Dipyridamole.
Dosage:
The usual dose is determined by a healthcare professional based on individual needs. It is typically administered intravenously.
Indications:
Dipiridamol ampoules are indicated for use in patients requiring increased blood flow in certain situations. It may be used in combination with other medications.
Contraindications:
Do not use Dipiridamol if you have a known allergy to Dipyridamole or any of the ingredients in the product. Consult a healthcare provider for more information.
Directions:
Administer as directed by a healthcare professional. Follow all instructions carefully.
Scientific Evidence:
Dipyridamole, the active ingredient in Dipiridamol ampoules, is known for its antiplatelet and vasodilatory effects. It inhibits platelet aggregation and increases coronary blood flow. Studies have shown its efficacy in preventing thrombosis and improving blood circulation in various clinical conditions.
Additional Information:
Pharmacologically, Dipyridamole works by inhibiting the uptake of adenosine into platelets, leading to increased levels of extracellular adenosine. This results in vasodilation and inhibition of platelet aggregation, contributing to its antiplatelet effects.
In clinical trials, Dipiridamol has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of thrombotic events in patients with coronary artery disease. Its combination with other antiplatelet agents has shown synergistic effects in preventing cardiovascular events. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Compared to similar drugs, Dipiridamol has shown comparable efficacy with a favorable safety profile. Its unique mechanism of action makes it a valuable addition to cardiovascular treatment regimens.