Description
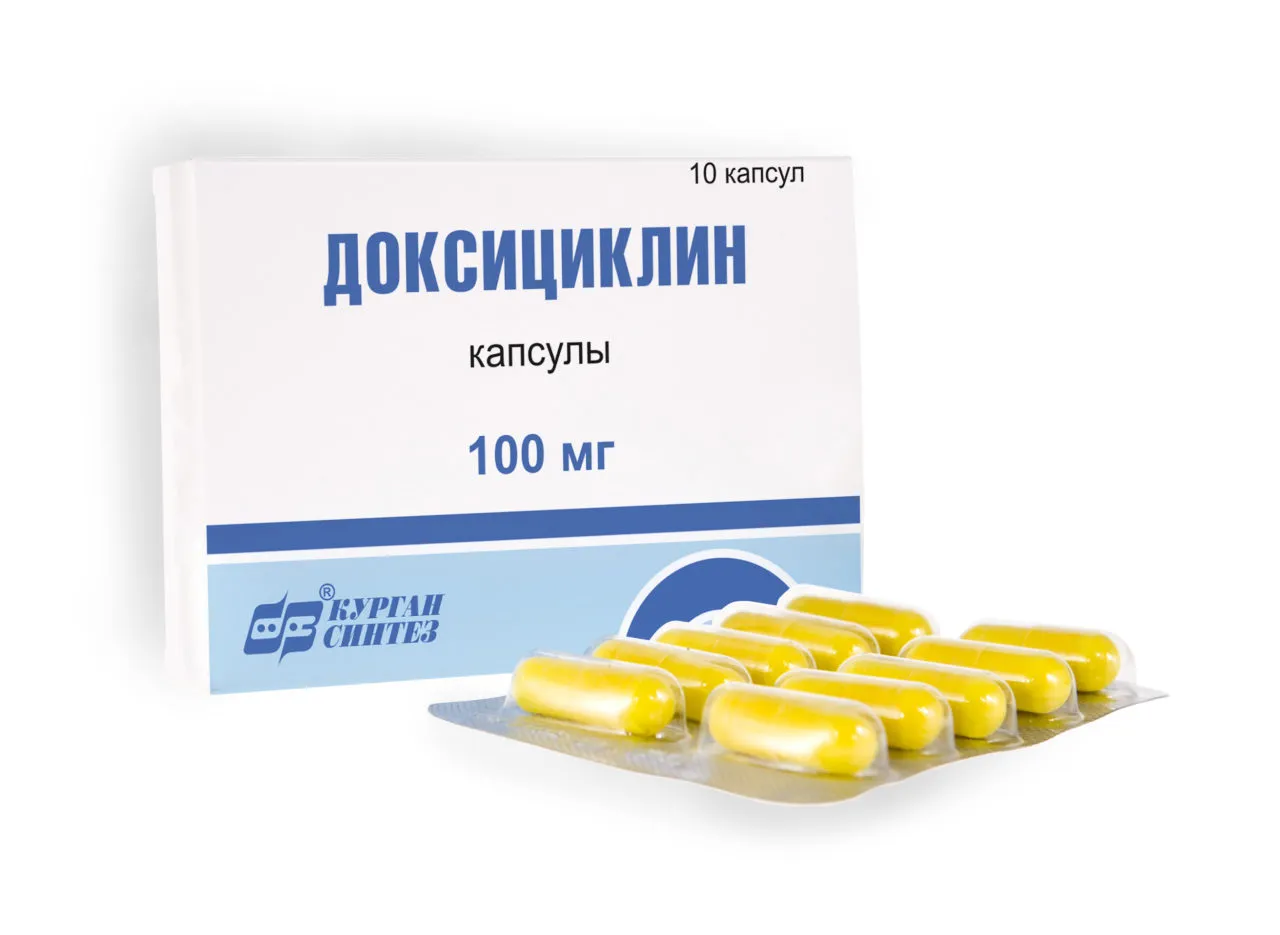
Doxiciclin (Doxycycline) Capsules 0.1 №10
Ingredients
Active Ingredient: Each capsule contains Doxycycline 0.1g.
Dosage
Dosage: The typical dosing regimen involves an initial dose of 200mg on the first day, either as a single dose or divided into two doses, followed by a maintenance dose of 100mg daily. Individualized dosing should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Indications
Indications: Doxycycline is indicated for the treatment of various infections caused by susceptible bacterial strains.
Contraindications
Contraindications: This medication should not be used in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to doxycycline or other tetracyclines.
Directions
Directions: Swallow the capsule whole with a full glass of water. Avoid crushing or chewing the capsule.
Scientific Evidence
Doxycycline, the active component in Doxiciclin capsules, has been extensively researched for its efficacy in combating a broad spectrum of bacterial infections. Studies published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy have demonstrated doxycycline’s effectiveness against various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, highlighting its versatility as an antibiotic choice.
Additional Information
Doxiciclin capsules are generally well-tolerated by patients and exhibit a favorable safety profile when used as directed. Completing the full course of treatment as prescribed by a healthcare provider is crucial to achieve optimal outcomes and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance.
Pharmacological Effects: Doxycycline exerts its action by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, thereby impeding bacterial growth and proliferation. This broad-spectrum antibiotic demonstrates efficacy against a diverse array of pathogens.
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials have showcased the efficacy of doxycycline in treating various infections such as respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Comparative studies have indicated that doxycycline is as effective as other antibiotics while exhibiting a more favorable side effect profile.