Description
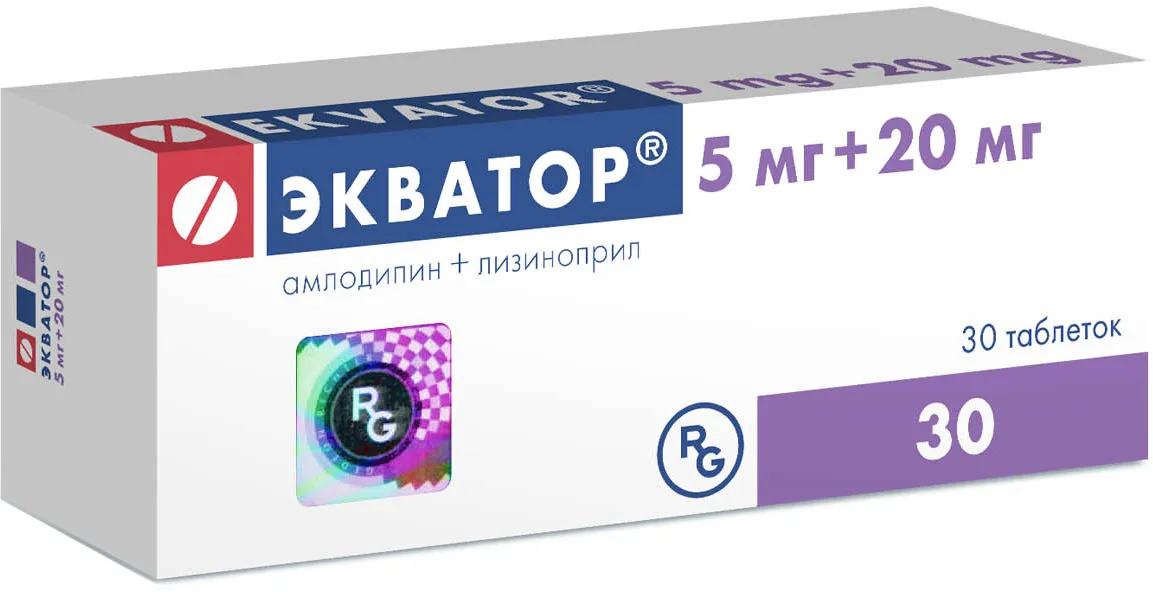
Ecvator (Lisinopril, Amlodipine) 20 mg/5 mg Tablets №30
Composition:
Each tablet contains 20 mg of lisinopril and 5 mg of amlodipine.
Mechanism of Action:
Ecvator combines the effects of lisinopril, an ACE inhibitor, and amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, to provide a dual mechanism of action for blood pressure control.
Pharmacological Properties:
The combination of lisinopril and amlodipine helps in lowering blood pressure by different mechanisms, leading to enhanced antihypertensive effects.
Indications for Use:
Ecvator tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension to lower blood pressure.
Contraindications:
Do not use Ecvator if you are allergic to any of the ingredients, have a history of angioedema related to previous ACE inhibitor therapy, or are pregnant.
Side Effects:
Common side effects may include dizziness, headache, edema, and cough. If you experience any severe side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Usage Instructions:
The usual recommended dose is one tablet per day, or as directed by a healthcare professional. Take Ecvator tablets by mouth with or without food.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Studies have shown that the combination therapy of lisinopril and amlodipine in Ecvator is more effective in reducing blood pressure compared to either drug alone.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Ecvator can be used in adult patients with hypertension. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for elderly patients or those with renal impairment.
Storage Conditions and Shelf Life:
Store Ecvator in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use the medication if expired.
Packaging Description:
Ecvator is available in a pack of 30 tablets. The packaging is designed to protect the tablets from moisture and ensure product integrity.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Research has demonstrated the efficacy and safety of Ecvator in managing hypertension, with significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels. Clinical trials have shown positive outcomes with low incidence of adverse effects.