Description
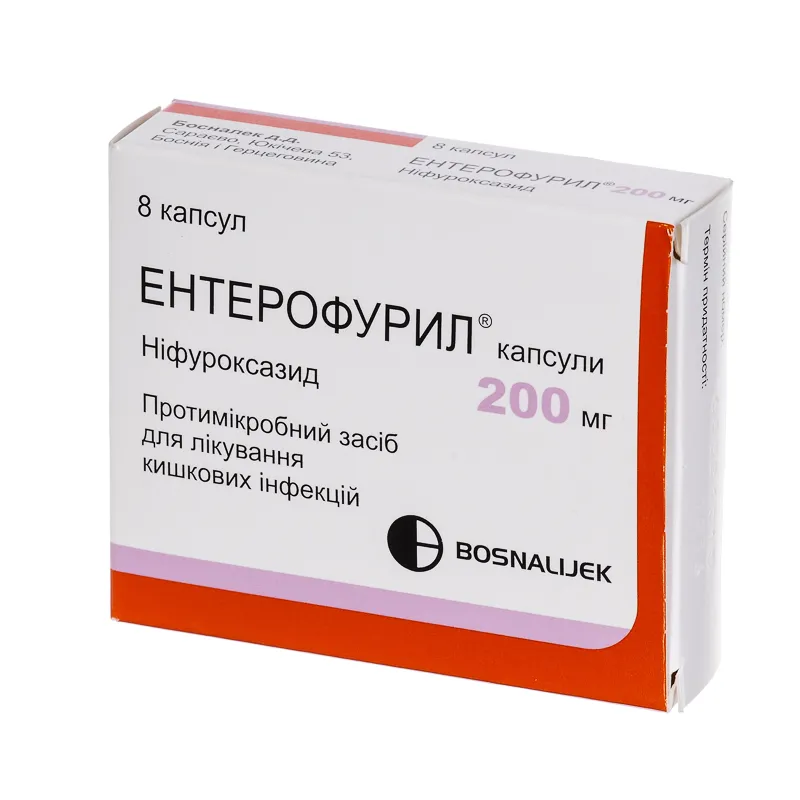
Enterofuril (Nifuroxazide) Capsules 200 mg. №8
Ingredients
Each capsule contains 200 mg of nifuroxazide as the active ingredient.
Mechanism of Action
Nifuroxazide, the active ingredient in Enterofuril, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria in the intestines.
Pharmacological Properties
Enterofuril capsules exert their therapeutic effects through the antibacterial action of nifuroxazide, targeting bacterial pathogens responsible for acute diarrhea.
Indications for Use
Enterofuril capsules are indicated for the treatment of acute diarrhea of bacterial origin.
Contraindications
Avoid using Enterofuril capsules if you have a known allergy to nifuroxazide or any other components of the product.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Enterofuril may include mild gastrointestinal disturbances. Consult your healthcare provider if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Usage Instructions
The typical dosage for adults and children above 12 years is 1-2 capsules taken four times daily. Swallow the capsules whole with water, without crushing or chewing them.
Benefits Compared to Analogues
Enterofuril offers a favorable safety profile and efficacy in treating bacterial diarrhea, distinguishing it as a preferred option over some conventional antibiotics.
Suitable Patient Groups
Enterofuril can be administered to various patient populations, including children and the elderly, under appropriate medical supervision.
Storage and Shelf Life
Store Enterofuril capsules in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use expired products.
Packaging Description
Enterofuril capsules are available in packs containing 8 capsules of 200 mg strength each, ensuring convenient dosing for the prescribed regimen.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness
Nifuroxazide has demonstrated clinical efficacy in reducing the duration and severity of symptoms in patients with bacterial diarrhea. Its role as a reliable treatment option is supported by scientific research.