Description
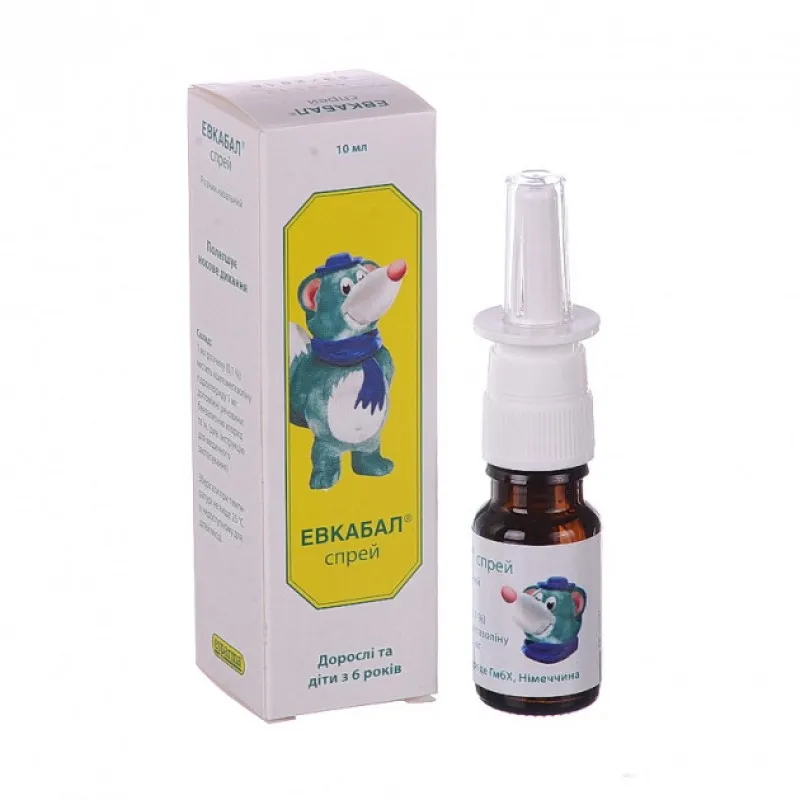
Eucabal (Acetylcysteine) Nasal Spray 1 mg/ml – 10 ml Vial №1
Composition
Active ingredient: Acetylcysteine 1 mg/ml
Mechanism of Action
Acetylcysteine, the active ingredient in Eucabal nasal spray, acts as a mucolytic agent by disrupting disulfide bonds in mucoproteins. This action results in the breakdown of mucus viscosity, facilitating easier clearance of respiratory secretions.
Pharmacological Properties
Eucabal nasal spray containing acetylcysteine exhibits mucolytic and antioxidant properties. Acetylcysteine helps in reducing the thickness of mucus, making it less adhesive and promoting expectoration. Additionally, its antioxidant effects contribute to mitigating oxidative stress in the airways.
Indications for Use
Eucabal nasal spray is indicated for the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion and to aid in the removal of mucus from the nasal passages in conditions such as rhinitis, sinusitis, and common cold.
Contraindications
Do not use Eucabal nasal spray if you have a known hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine or any other components of the formulation. Consult a healthcare provider before use if uncertain about allergies.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Eucabal nasal spray may include nasal irritation, sneezing, or transient burning sensation. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if experiencing severe allergic reactions or persistent adverse effects.
Usage Instructions
Dosage: Administer 1 spray into each nostril 2-3 times daily or as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Shake the vial well before each use. Avoid deep inhalation post-spraying to prevent irritation.
Benefits over Analogues
Eucabal nasal spray with acetylcysteine offers a dual-action approach by effectively clearing nasal congestion and promoting mucus clearance, thereby providing comprehensive relief compared to standard nasal decongestants.
Suitable Patient Groups
Eucabal nasal spray is suitable for adults, adolescents, and children over a certain age (as determined by a healthcare provider). Elderly individuals and individuals with respiratory conditions can also benefit from the mucolytic and decongestant properties of acetylcysteine.
Storage and Shelf Life
Store Eucabal nasal spray at room temperature away from direct sunlight and moisture. Check the product packaging for specific storage instructions. Ensure proper sealing to maintain product integrity. The shelf life of the product is as indicated on the packaging.
Packaging Description
Eucabal nasal spray is supplied in a 10 ml vial, ensuring convenient and accurate dosing. The packaging is designed to maintain product sterility and integrity throughout its shelf life.