Description
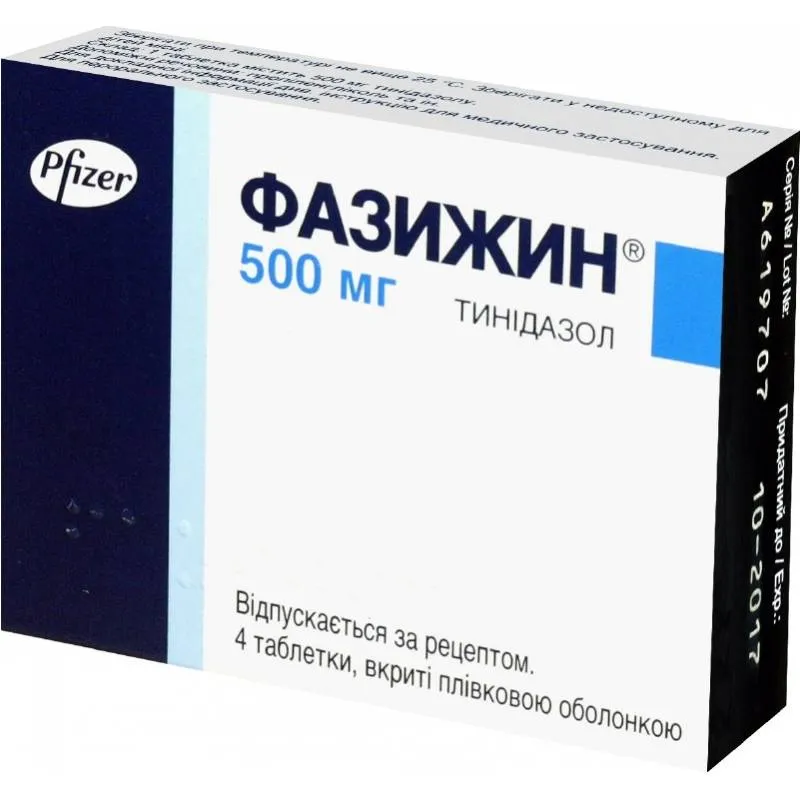
Fazijin (Tinidazolum) Coated Tablets 500 mg. №4
Ingredients
Each coated tablet contains 500 mg of tinidazole.
Dosage
The usual dosage for adults is 2 g as a single dose or in divided doses over a day.
Indications
Fazijin tablets are indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of various organisms.
Contraindications
Avoid Fazijin tablets if you have a history of hypersensitivity to tinidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
Directions
Take Fazijin tablets by mouth with food to reduce stomach upset.
Scientific Evidence
Fazijin (tinidazolum) has shown significant efficacy in treating various infections, including protozoal and anaerobic bacterial infections.
Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of tinidazole in the treatment of trichomoniasis, giardiasis, and amebiasis.
Additional Information
It is important to complete the full course of Fazijin tablets as prescribed by your healthcare provider to ensure the infection is fully treated.
Consult your doctor if you experience any severe side effects while taking Fazijin tablets.
Pharmacological Effects
Tinidazole, the active ingredient in Fazijin tablets, exerts its antimicrobial effects by disrupting the DNA structure of pathogens, leading to their death.
This mechanism of action makes tinidazole effective against a wide range of protozoa and anaerobic bacteria.
Clinical Trials and Comparative Effectiveness
Clinical trials have shown that Fazijin tablets are comparable in efficacy to other nitroimidazoles in the treatment of various infections.
In comparative studies, Fazijin demonstrated similar or superior effectiveness in eradicating pathogens compared to standard treatments.