Description
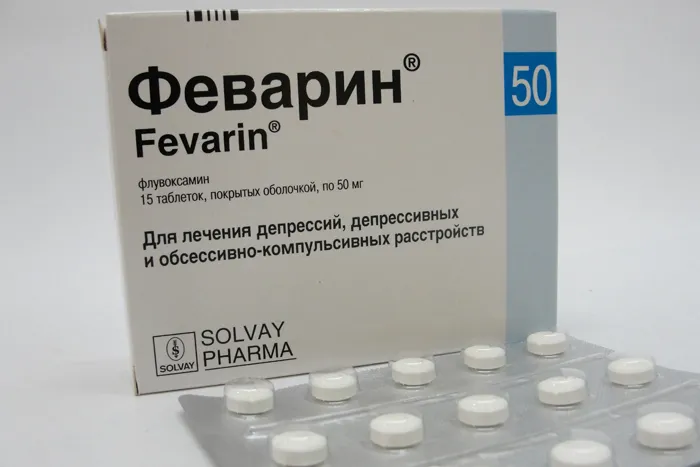
Fevarin (Fluvoxamine) Coated Tablets 100 mg. №15
Ingredients:
Each coated tablet contains 100 mg of fluvoxamine as the active ingredient.
Mechanism of Action:
Fluvoxamine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), increases serotonin levels in the brain. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter, regulates mood, emotions, and behavior. By inhibiting serotonin reuptake, fluvoxamine alleviates symptoms of depression, OCD, and anxiety disorders.
Pharmacological Properties:
Fluvoxamine acts by selectively inhibiting serotonin reuptake in the central nervous system, leading to enhanced serotonergic activity. It has a high affinity for the serotonin transporter and minimal effects on other neurotransmitters.
Indications for Use:
Fevarin tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and social anxiety disorder (SAD) in adults.
Contraindications:
Do not use Fevarin if you are hypersensitive to fluvoxamine or if you are concurrently taking thioridazine or pimozide due to potential drug interactions.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of Fevarin may include drowsiness, dizziness, gastrointestinal disturbances, insomnia, and sexual dysfunction. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience severe or persistent side effects.
Usage Instructions:
The recommended dose for adults is one 100 mg tablet daily, preferably taken in the evening with food. Swallow the tablet whole with water and adhere to your healthcare provider’s guidance.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Fevarin offers efficacy in treating MDD, OCD, and SAD with a favorable tolerability profile. Its specific serotonin reuptake inhibition mechanism distinguishes it from other antidepressants, providing a targeted approach to managing these conditions.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Fevarin is suitable for adult patients with MDD, OCD, or SAD. Caution is advised in geriatric populations due to potential sensitivity to side effects. Pediatric use should be determined by a healthcare professional based on individual considerations.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Store Fevarin at controlled room temperature away from moisture and heat. Check the packaging for the expiration date and do not use the product beyond this date.
Packaging Description:
Fevarin is available in blister packs containing 15 coated tablets of 100 mg strength. The packaging should be intact and undamaged upon purchase.
Scientific Evidence:
Fluvoxamine has demonstrated efficacy in treating depression and anxiety disorders. Studies have shown its superiority over placebo in reducing OCD symptoms and its effectiveness in managing major depressive disorder. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized treatment recommendations.
Additional Information:
- Fevarin may cause drowsiness or dizziness. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you understand its effects on you.
- Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including supplements, to prevent potential interactions.
- Allow time for Fevarin to exert its full therapeutic effects. Do not discontinue treatment abruptly without medical guidance.