Description
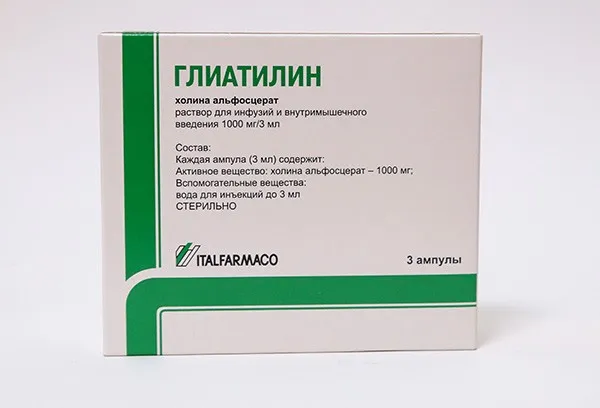
Gliatilin Solution for Injections 4 ml Ampoules №3
Ingredients
Gliatilin solution for injections contains the active ingredient acetyl-L-carnitine, which plays a crucial role in cellular energy production and neurotransmitter synthesis.
Dosage
The recommended dosage of Gliatilin solution for injections is determined by a healthcare professional based on individual needs. It is typically administered via intramuscular injection.
Indications
Gliatilin solution for injections is indicated for the treatment of cognitive disorders, memory impairment, and neurological conditions associated with aging or neurodegenerative diseases.
Contraindications
Do not use Gliatilin solution for injections if you are allergic to acetyl-L-carnitine or any other ingredients in the formulation. Consult with a healthcare provider before use.
Directions
Administer Gliatilin solution for injections as directed by a healthcare professional. Follow the recommended dosage and injection technique for optimal results.
Scientific Evidence
Acetyl-L-carnitine, the active ingredient in Gliatilin solution for injections, has been extensively studied for its neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties. Research suggests that acetyl-L-carnitine may improve cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health by enhancing energy metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis (Montgomery et al., 2003).
Additional Information
Pharmacologically, Gliatilin solution for injections acts by supporting mitochondrial function and enhancing the production of acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning. By optimizing cellular energy metabolism and neurotransmission, Gliatilin promotes cognitive function and neuronal health.
Compared to other cognitive enhancers, Gliatilin solution for injections stands out for its multifaceted approach to brain health. Its ability to improve energy production, neurotransmitter levels, and neuroprotection sets it apart as a comprehensive solution for cognitive support.