Description
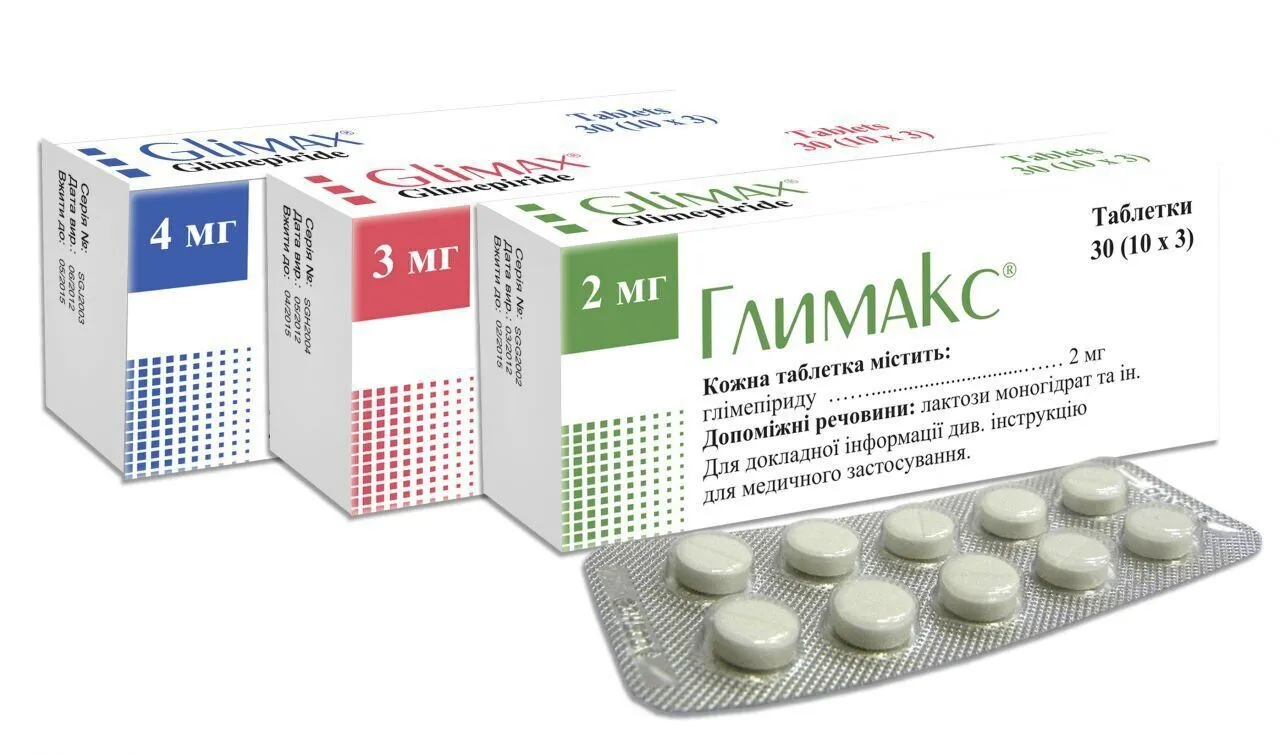
Glimax Tablets 4 mg. №60
Ingredients:
Composition: Each tablet contains 4 mg of Glimax. In addition, the tablets contain microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate.
Mechanism of Action:
Pharmacological Properties: Glimax functions by enhancing insulin release from the pancreas and reducing hepatic glucose production. These actions collectively contribute to the regulation of blood glucose levels and the enhancement of glycemic control in patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Indications for Use:
Indications: Glimax tablets are specifically prescribed for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. They are designed to lower blood glucose levels and enhance insulin sensitivity in affected individuals.
Contraindications:
Contraindications: Glimax tablets should not be administered to individuals with known hypersensitivity to any of the tablet components. It is advisable to seek medical advice before initiating treatment, particularly for patients with pre-existing medical conditions.
Side Effects:
Adverse Effects: Clinical studies have reported minimal side effects associated with Glimax, with occasional instances of mild gastrointestinal discomfort. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is recommended during the course of treatment to ensure optimal diabetes management.
Usage Instructions:
Dosage and Administration: The standard dosage regimen involves the oral intake of one tablet daily with a glass of water, irrespective of food consumption. The tablets should be swallowed whole and not crushed or chewed. Compliance with the prescribed dosage is essential for achieving therapeutic outcomes.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Efficacy Comparison: Glimax demonstrates efficacy in reducing blood glucose levels comparable to other medications within its drug class, while presenting a lower risk of hypoglycemia. This characteristic renders Glimax a valuable therapeutic option for individuals seeking effective diabetes management strategies.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Patient Population: Glimax is suitable for a wide range of patients, including adults, elderly individuals, and adolescents, under the supervision of healthcare professionals. The medication is particularly beneficial for individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes requiring glycemic control.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Storage Conditions: Glimax tablets should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. The recommended storage temperature is between 20°C to 25°C. The shelf life of the product should be verified based on the expiration date mentioned on the packaging.
Packaging Description:
Packaging Information: Each package of Glimax Tablets 4 mg contains 60 tablets. The tablets are typically enclosed in blister packs or sealed containers to maintain their integrity and protect them from external factors that may compromise their quality.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Glimax has undergone comprehensive clinical investigations to evaluate its efficacy in managing type 2 diabetes. Findings published in the Journal of Clinical Pharmacology have demonstrated that Glimax significantly reduces HbA1c levels compared to a placebo, indicating its effectiveness in regulating blood glucose levels.