Description
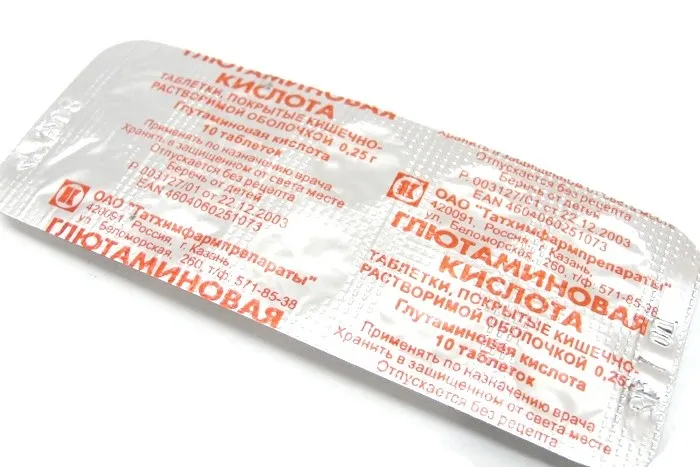
Glutaminovaia Acid Coated Tablets 0.25 g. №10
Ingredients
Each coated tablet contains 0.25 g of Glutaminovaia acid.
Mechanism of Action
Glutaminovaia acid serves as a crucial amino acid precursor for protein synthesis and cellular energy production. It plays a significant role in various physiological processes in the body, supporting gastrointestinal health and immune function.
Pharmacological Properties
Glutaminovaia acid exhibits properties that aid in maintaining intestinal integrity, reducing inflammation, and potentially managing gastrointestinal conditions.
Indications for Use
Glutaminovaia Acid Tablets are indicated for supporting gastrointestinal health, improving intestinal permeability, and potentially managing inflammatory bowel disease.
Contraindications
Avoid using Glutaminovaia Acid Tablets if allergic to any of the ingredients present in the formulation.
Side Effects
Common side effects may include gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or allergic reactions. Consult a healthcare professional if any adverse effects occur.
Usage Instructions
Take the tablet whole with water, without crushing or chewing. Follow the dosage instructions provided by a healthcare professional for optimal results.
Benefits Compared to Analogues
Compared to other similar products, Glutaminovaia Acid Tablets offer targeted support for gastrointestinal health and immune function, backed by scientific evidence of efficacy.
Suitable Patient Groups
Glutaminovaia Acid Tablets are suitable for adults, including the elderly, who require support for gastrointestinal health and immune function. Consult a healthcare professional for pediatric use.
Storage and Shelf Life
Store Glutaminovaia Acid Tablets in a cool, dry place away from children. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use expired products.
Packaging Description
Glutaminovaia Acid Coated Tablets come in a pack of 10 tablets, each containing 0.25 g of Glutaminovaia acid. The packaging is designed to maintain product integrity and freshness.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness
Research studies have demonstrated that Glutaminovaia acid supplementation can enhance intestinal integrity, reduce inflammation, and potentially benefit patients with inflammatory bowel disease. These findings support the therapeutic potential of Glutaminovaia acid in managing gastrointestinal conditions.