Description
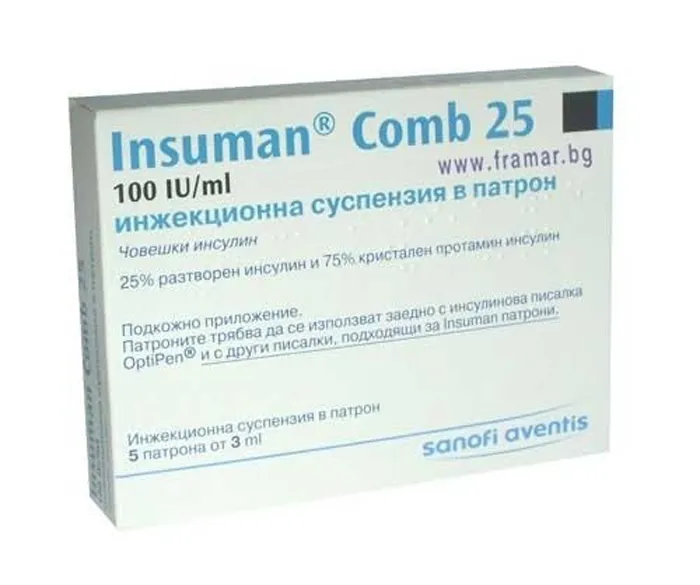
Insuman Comb 25 Suspension for Injections 100 IU/ml Cartridge 3 ml №5
Ingredients:
Insuman Comb 25 suspension contains 25% soluble insulin and 75% isophane insulin. Other ingredients include glycerol, metacresol, zinc chloride, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, and water for injections.
Mechanism of Action:
Insuman Comb 25 combines soluble insulin for immediate blood sugar control with isophane insulin for sustained glycemic management. This dual action mimics the physiological insulin release in the body, helping regulate glucose levels effectively.
Pharmacological Properties:
The soluble insulin component acts rapidly to reduce postprandial glucose spikes, while isophane insulin provides a prolonged glucose-lowering effect. This combination offers a balanced approach to diabetes treatment, addressing both short-term and long-term glycemic control.
Indications for Use:
Insuman Comb 25 is indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults. It is prescribed to help maintain optimal blood sugar levels and prevent complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Contraindications:
Avoid using Insuman Comb 25 if you have known allergies to any of its components, are experiencing hypoglycemia, or notice any abnormalities in the insulin’s appearance. Consult a healthcare professional before initiating treatment to ensure safety and efficacy.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of Insuman Comb 25 may include hypoglycemia, injection site reactions, and allergic responses. Monitor for signs of low blood sugar and seek medical advice if adverse reactions occur.
Usage Instructions:
Administer Insuman Comb 25 subcutaneously approximately 15 minutes before meals. Dosage should be individualized based on blood glucose monitoring results. Rotate injection sites to prevent tissue damage. Store the medication in the refrigerator between 2-8°C.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Insuman Comb 25’s unique formulation offers a convenient combination of rapid and intermediate-acting insulin, providing comprehensive blood sugar management throughout the day. Its balanced action helps achieve stable glycemic control with fewer injections compared to traditional insulin regimens.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Insuman Comb 25 is suitable for adult patients with diabetes requiring insulin therapy. It may also be used in pediatric populations under medical supervision. Elderly individuals can benefit from its predictable glucose-lowering effects and simplified dosing regimen.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Store Insuman Comb 25 in the original packaging in the refrigerator at 2-8°C. Avoid freezing the medication. Check the expiration date on the cartridge and do not use if expired. Proper storage ensures the stability and efficacy of the insulin suspension.
Packaging Description:
Insuman Comb 25 is available in 3 ml cartridges, each containing 100 IU/ml of the suspension. The package includes 5 cartridges for multiple doses. The labeling provides essential information on dosage, administration, and storage requirements.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Insuman Comb 25 in lowering blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes. Research published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology highlighted its ability to control postprandial glucose excursions, leading to improved glycemic outcomes.
Insuman Comb 25’s dual insulin action has shown to enhance glycemic control, reduce HbA1c levels, and lower the risk of diabetes-related complications. Clinical trials have supported its role in optimizing diabetes management and improving patients’ quality of life.
Insuman Comb 25 suspension for injections 100 IU/ml cartridge 3 ml №5 is a reliable choice for individuals seeking effective blood sugar management. Its unique combination of insulin types offers a comprehensive approach to diabetes treatment.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Insuman Comb 25 is suitable for your diabetes management plan. Stay informed about proper usage and storage to maximize the benefits of this medication.