Description
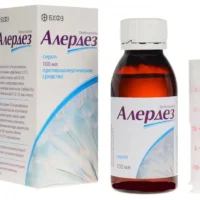
L-cet (Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride) Syrup 2.5 mg/5 ml – 100 ml Vial
Composition
Active Ingredient: Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride
Other Ingredients: [List other ingredients here]
Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, exerts its pharmacological effects by selectively antagonizing the H1 histamine receptor. This action inhibits the release of histamine, thereby mitigating allergic symptoms.
Pharmacological Properties
Levocetirizine demonstrates high affinity and selectivity for the H1 receptor, leading to potent antihistaminic effects. It has a longer duration of action compared to cetirizine and is associated with a lower incidence of sedation.
Indications for Use
L-cet syrup is indicated for the symptomatic relief of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria in adults and children.
Contraindications
Do not administer L-cet syrup to individuals with a known hypersensitivity to levocetirizine or any of the formulation components.
Side Effects
Common side effects may include drowsiness, headache, dry mouth, and fatigue. Consult a healthcare professional if any adverse reactions occur.
Usage Instructions
For adults and children above 6 years, the typical dosage is 5 mg once daily. Dosage adjustments are necessary for pediatric patients under 6 years and should be determined by a healthcare provider.
Benefits Compared to Analogues
Levocetirizine has demonstrated superior efficacy and tolerability compared to other antihistamines, with a reduced risk of sedation and similar or improved symptom relief.
Suitable Patient Groups
L-cet syrup is suitable for use in both pediatric and geriatric populations. Dosage adjustments may be required based on age and individual health conditions.
Storage and Shelf Life
Store L-cet syrup at room temperature, away from moisture and heat. Ensure the product is kept out of reach of children. Check the expiration date before use.
Packaging Description
The product is supplied in a 100 ml vial containing Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride syrup at a concentration of 2.5 mg/5 ml. The packaging should be intact and properly sealed upon purchase.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness
Studies have shown that Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride effectively alleviates symptoms of allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion, highlighting its role as a valuable therapeutic option.