Description
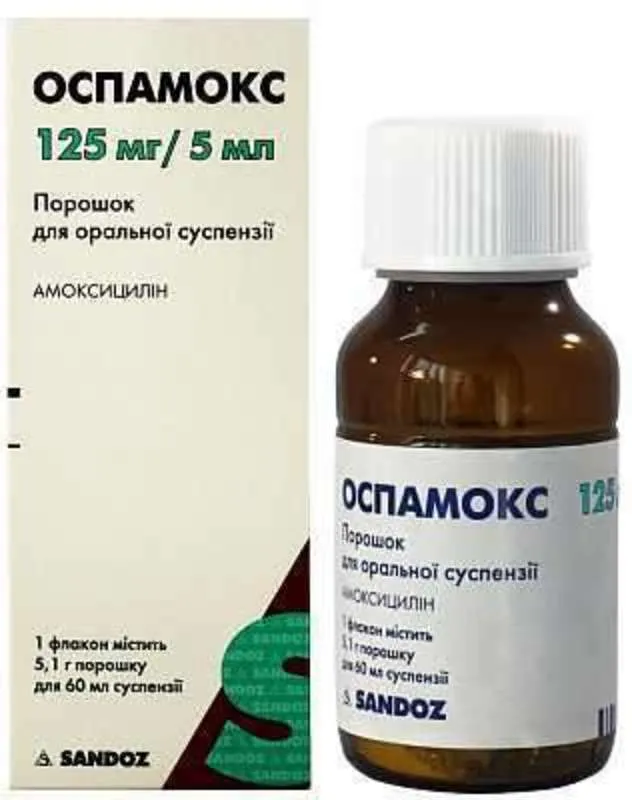
Ospamox Powder for Suspension 125 mg/5 ml. 60 ml Vial
Ingredients
- Each 5 ml of the suspension contains 125 mg of amoxicillin (as amoxicillin trihydrate) as the active ingredient.
Dosage
- The dosage of Ospamox should be prescribed by a healthcare professional based on the individual’s condition and age. It is usually administered every 8 hours. Shake the suspension well before each use.
Indications
- Ospamox is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections caused by susceptible strains. These may include respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and more.
Contraindications
- Do not use Ospamox if you are allergic to amoxicillin or other penicillins. Consult with a healthcare provider if you have a history of allergic reactions.
Directions
- Mix the prescribed amount of Ospamox powder with water to prepare the suspension. Administer the suspension orally as directed. Complete the full course of treatment even if you feel better.
Scientific Evidence
- Studies have shown the efficacy of amoxicillin in treating various bacterial infections. Research published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy demonstrated the effectiveness of amoxicillin in combating common respiratory pathogens.
Additional Information
- It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full treatment course to ensure the best outcomes. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any adverse reactions while taking Ospamox.
Pharmacologically, Ospamox works by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls, leading to bacterial cell death. This action targets a wide range of bacteria, making it a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Clinical trials have shown Ospamox to be as effective as other commonly used antibiotics in the treatment of various infections. Its safety profile and efficacy make it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers.