Description
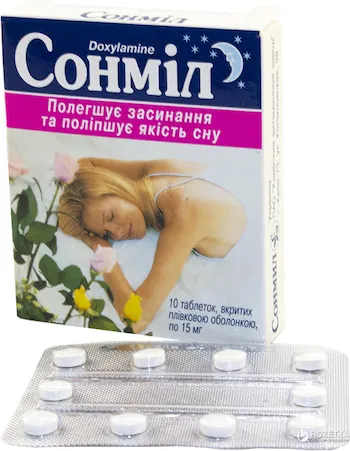
Sonmil (Doxylamine Succinate) Coated Tablets 15 mg. №10
Ingredients:
- Each coated tablet contains 15 mg of doxylamine succinate.
- Other ingredients include lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and a coating of hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
Dosage:
The recommended dosage for adults is one tablet at bedtime. Do not exceed the stated dose.
Indications:
Sonmil tablets are indicated for the short-term relief of insomnia. They help to reduce the time taken to fall asleep and improve sleep maintenance.
Contraindications:
Do not use Sonmil tablets if you are allergic to doxylamine succinate or any other ingredients in the product. Avoid use in individuals with narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention, severe liver disease, or respiratory conditions like asthma.
Directions:
Take one tablet orally with water 30 minutes before bedtime. Do not crush or chew the tablet. Avoid alcohol and other sedatives while using Sonmil.
Scientific Evidence:
Studies have shown that doxylamine succinate, the active ingredient in Sonmil tablets, is effective in promoting sleep onset and improving sleep quality. A review published in the American Journal of Therapeutics concluded that doxylamine succinate is a safe and well-tolerated option for the management of insomnia.
Additional Information:
Sonmil tablets should be used for short-term relief of insomnia. Prolonged use may lead to tolerance and dependence. Consult a healthcare professional if sleep problems persist. Keep out of reach of children.
Pharmacological Effects:
Doxylamine succinate, an antihistamine, exerts its sedative effects by antagonizing the histamine H1 receptors in the brain. This action leads to drowsiness and facilitates the onset of sleep. Additionally, it possesses anticholinergic properties, contributing to its sedative effects.
Clinical Trials and Comparative Effectiveness:
In comparative studies, doxylamine succinate has shown similar efficacy to other sedating antihistamines in improving sleep parameters. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine demonstrated that doxylamine succinate significantly reduced the time to fall asleep and increased total sleep time compared to placebo.