Description
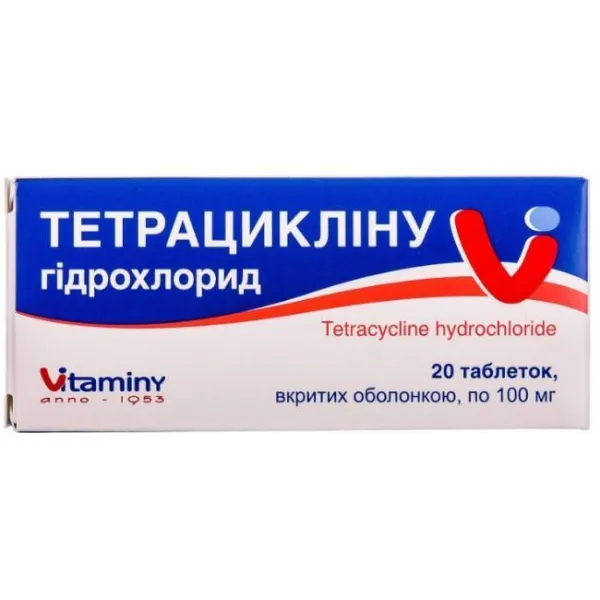
Tetracycline Hydrochloride Coated Tablets 100 mg №20
Ingredients:
- Each coated tablet contains 100 mg of Tetracycline Hydrochloride.
Dosage:
- The usual dosage is 250-500 mg every 6 hours.
- Dosage may vary based on the condition being treated.
Indications:
- Tetracycline Hydrochloride coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections.
- Commonly used for respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and more.
Contraindications:
- Avoid use if pregnant, breastfeeding, or have a history of kidney disease.
Directions:
- Take as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Usually taken on an empty stomach with a full glass of water to prevent stomach upset.
Scientific Evidence:
Tetracycline Hydrochloride is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. Effective in treating bacterial infections like acne vulgaris, chlamydia, and respiratory tract infections.
Additional Information:
- Complete the full course of treatment as prescribed.
- Failure to do so may lead to incomplete treatment and antibiotic resistance.
- Inform your healthcare provider about all medications before use.