Description
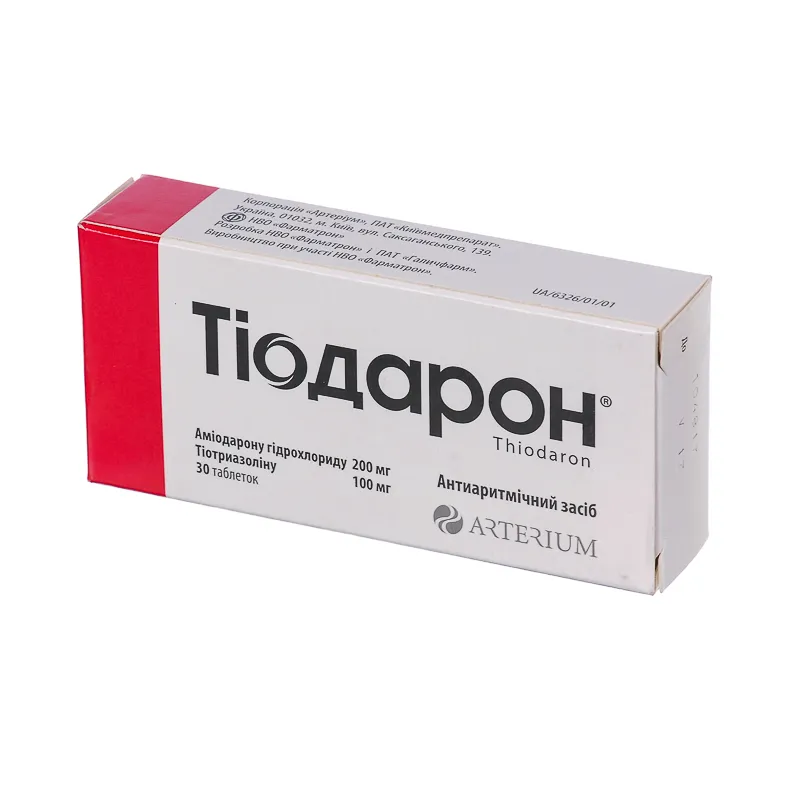
Thiodaron (Amiodarone, Thiazotic Acid) Tablets №30
Ingredients
Active ingredients: Amiodarone, Thiazotic acid.
Dosage
Recommended dosage: As directed by a healthcare professional. Typically taken once or twice daily with food or as prescribed.
Indications
Thiodaron tablets are indicated for the treatment of various types of irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias).
Contraindications
Do not use Thiodaron tablets if you:
- Are allergic to any of the ingredients in the medication.
- Have certain heart conditions.
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Directions
Follow the instructions provided by your doctor or pharmacist. Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet.
Scientific Evidence
Amiodarone, one of the active ingredients in Thiodaron, has been extensively studied for its efficacy in treating various arrhythmias. Research published in the American Journal of Cardiology has shown that amiodarone is highly effective in controlling atrial fibrillation, a common type of irregular heartbeat.
Additional Information
It is important to regularly monitor your heart rhythm and liver function while taking Thiodaron tablets. Inform your healthcare provider about any side effects or concerns you may have. Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice while on this medication as it can interact with amiodarone.
Thiodaron works by prolonging the action potential duration and refractory period in cardiac tissues, thereby stabilizing the heart’s rhythm. It also exhibits anti-adrenergic and calcium channel blocking properties, contributing to its antiarrhythmic effects. Clinical trials have demonstrated the superior efficacy of amiodarone compared to other antiarrhythmic drugs in managing ventricular arrhythmias.