Description
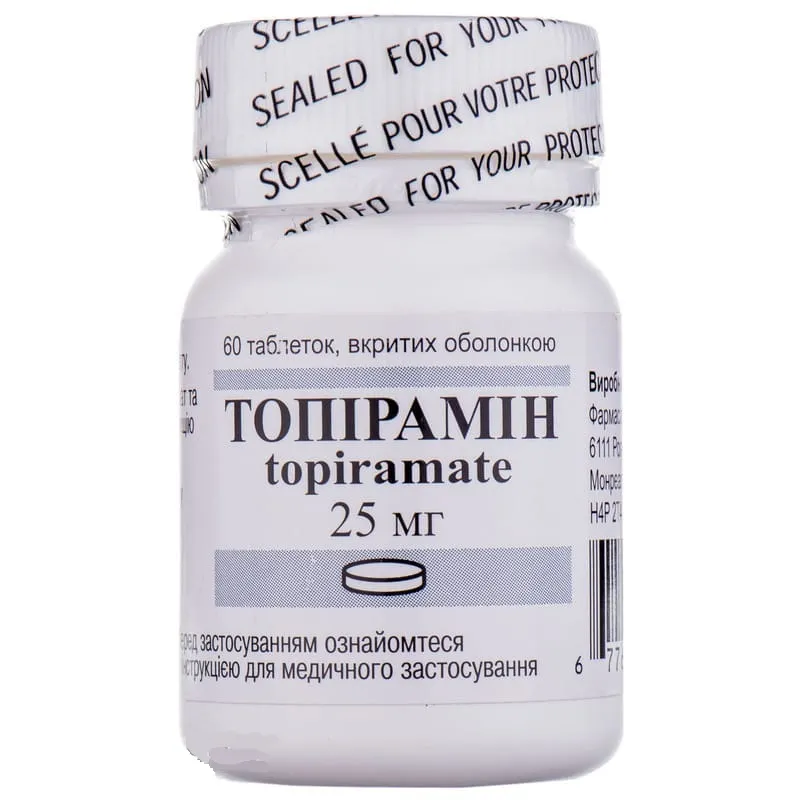
Topiramin (Topiramate) Coated Tablets 25 mg. №60 Vial
Ingredients
- Active ingredient: Topiramate 25 mg.
- Other ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, macrogol 400, titanium dioxide, talc.
Dosage
Recommended dosage: The usual starting dose is 25 mg once daily in the evening. Dosage may be increased by 25-50 mg/day every week based on response. Maximum recommended dose is 400 mg/day.
Indications
Topiramin (Topiramate) coated tablets are indicated for the treatment of epilepsy in both adults and children. It is also used for the prevention of migraine headaches.
Contraindications
Do not use Topiramin (Topiramate) coated tablets if you are allergic to topiramate or any of the other ingredients. It is contraindicated in patients with metabolic acidosis, severe renal impairment, and certain types of glaucoma.
Directions
Take Topiramin (Topiramate) coated tablets orally with or without food, as directed by your healthcare provider. Swallow the tablets whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablets.
Scientific Evidence
Topiramate, the active ingredient in Topiramin tablets, has been extensively studied for its efficacy in the treatment of epilepsy and migraine. Research has shown that topiramate works by blocking voltage-dependent sodium channels, enhancing the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and inhibiting glutamate receptors. These mechanisms help to stabilize electrical activity in the brain, reducing the frequency and severity of seizures in epilepsy patients and preventing migraine attacks.
Additional Information
In clinical trials, Topiramin (Topiramate) coated tablets have demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing seizure frequency and improving quality of life in patients with epilepsy. The medication has also been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency of migraine headaches and improving migraine-related disability. Common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, and cognitive impairment. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare provider for proper management.
Overall, Topiramin (Topiramate) coated tablets 25 mg. offer a well-established treatment option for epilepsy and migraine, backed by scientific evidence and clinical trials supporting its efficacy and safety profile.