Description
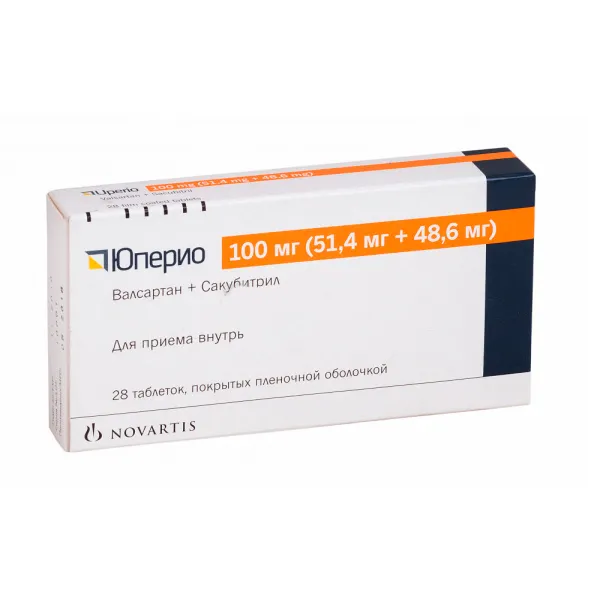
Uperio (Sacubitril, Valsartan) Coated Tablets 100 mg. №28
Ingredients
- Active ingredients: Sacubitril and Valsartan
Dosage
- Recommended dosage: 100 mg once daily
Indications
- Indicated for: Treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
Contraindications
- Contraindicated in: Patients with a history of angioedema related to previous ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy
Directions
- Administration: Swallow the tablet whole with water, with or without food
Scientific Evidence
Sacubitril/valsartan has shown significant benefits in reducing cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations compared to ACE inhibitors in patients with heart failure. The PARADIGM-HF trial demonstrated a 20% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization with sacubitril/valsartan.
Additional Information
- Uperio (sacubitril, valsartan) is a novel combination drug that acts to enhance the natriuretic peptide system while simultaneously blocking the harmful effects of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This dual mechanism of action results in vasodilation, diuresis, and improved cardiac function in heart failure patients.
- Clinical trials have shown that Uperio is well-tolerated and effective in reducing the risk of heart failure exacerbations and improving quality of life in patients with heart failure. It is considered a breakthrough in the management of heart failure and has the potential to significantly impact patient outcomes.