Description
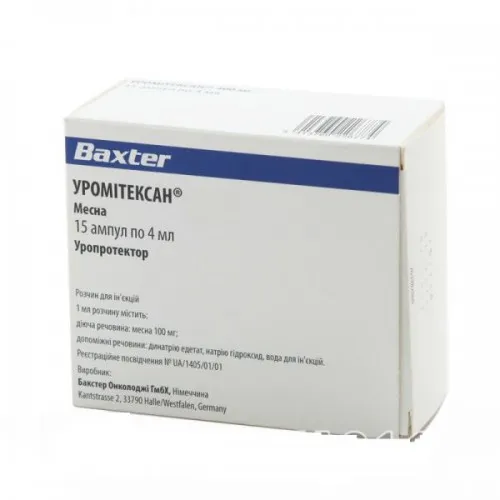
Uromitexan (Mesna) 400 mg Solution for Injections
Ingredients:
Each ampoule contains 400 mg of mesna in a 100 mg/ml solution for injections.
Dosage:
The usual adult dosage is 20% of the ifosfamide dose, administered as a bolus injection followed by a continuous infusion.
Indications:
Uromitexan is indicated for the prophylaxis of ifosfamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. It is used in conjunction with ifosfamide in cancer chemotherapy to reduce the risk of bladder toxicity.
Contraindications:
Do not use Uromitexan in patients with a known hypersensitivity to mesna or other inactive ingredients in the formulation. It should be used with caution in patients with a history of allergic reactions.
Directions:
Uromitexan is administered intravenously or intramuscularly under the supervision of a healthcare provider. Dosage and administration should be individualized based on the ifosfamide regimen.
Scientific Evidence:
Mesna, the active ingredient in Uromitexan, is a synthetic compound that acts as a cytoprotective agent by binding to and neutralizing the toxic metabolites of ifosfamide in the bladder. This mechanism helps prevent the development of hemorrhagic cystitis, a common side effect of ifosfamide therapy.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of mesna in reducing the incidence and severity of ifosfamide-induced bladder toxicity. A study published in the European Journal of Cancer showed that the prophylactic use of mesna significantly decreased the risk of hemorrhagic cystitis in cancer patients receiving ifosfamide-based chemotherapy.
Additional Information:
- Storage: Store Uromitexan at room temperature away from light and moisture.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience severe reactions.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Consult your doctor before using Uromitexan if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.