Description
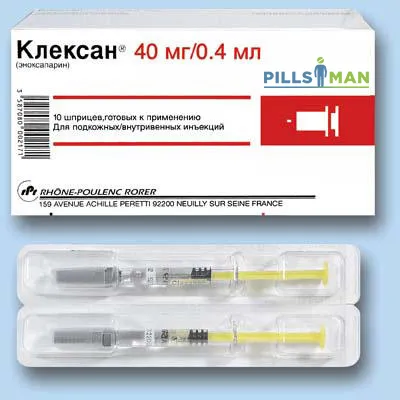
Clexane (Enoxaparin) Solution for Injections Syringe 40 mg, 0.4 ml, №10
Ingredients:
Each syringe contains 40 mg of enoxaparin sodium.
Mechanism of Action:
Enoxaparin, a low molecular weight heparin, acts by inhibiting the formation of blood clots.
Pharmacological Properties:
Enoxaparin exerts its anticoagulant effect by enhancing the inhibition of factor Xa. It also potentiates the inhibition of thrombin by antithrombin III.
Indications for Use:
Clexane is indicated for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in various conditions, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Contraindications:
Do not use Clexane in cases of active major bleeding or a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Side Effects:
Common side effects may include bleeding, bruising, and injection site reactions. Serious side effects include thrombocytopenia and allergic reactions.
Usage Instructions:
The usual dosage is 1 mg per kilogram of body weight, administered subcutaneously once daily. Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and avoid self-injection unless instructed.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Clexane is preferred over unfractionated heparin in many clinical scenarios due to its predictable anticoagulant effect and lower risk of side effects. It offers a more convenient dosing regimen and reduced monitoring requirements.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Clexane can be used in various patient populations, including adults, elderly individuals, and children under specific dosing regimens. Dosing adjustments may be necessary based on age and weight.
Storage Conditions and Shelf Life:
Store Clexane at recommended room temperature away from light and moisture. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use expired products.
Packaging Description:
Clexane is available in syringes containing 40 mg of enoxaparin sodium in 0.4 ml solution for injections. Each package contains 10 syringes for single-use.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Enoxaparin has demonstrated efficacy in preventing venous thromboembolism in various clinical settings, such as orthopedic surgery and medical patients at risk of clot formation. Clinical studies have shown significant reduction in clotting events with the use of enoxaparin.