Description
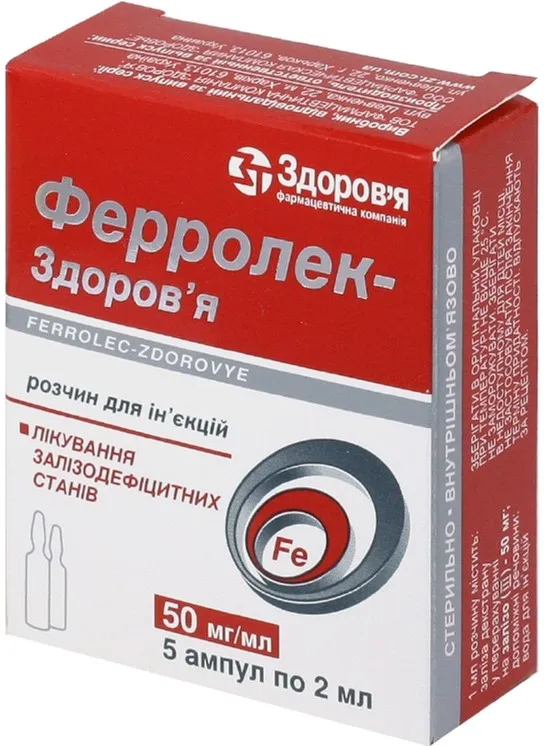
Ferrolek Solution for Injections Ampoules 50 mg/ml. 2 ml. №5
Ingredients:
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 50 mg of Ferrolek solution for injections.
Mechanism of Action:
Ferrolek solution replenishes iron stores in the body, facilitating hemoglobin synthesis and red blood cell production.
Pharmacological Properties:
Ferrolek solution functions as an iron supplement, aiding in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia by increasing hemoglobin levels and improving overall iron status.
Indications for Use:
Ferrolek solution is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adults. It is beneficial for restoring iron levels and enhancing hemoglobin concentrations in the blood.
Contraindications:
Avoid using Ferrolek solution if you have a hypersensitivity to any of its components. This product is contraindicated in individuals with hemochromatosis or hemosiderosis due to potential iron overload risks.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of Ferrolek solution may include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, and injection site reactions. Consult a healthcare professional if any adverse effects occur.
Usage Instructions:
The typical dosage involves administering 1-2 ampoules daily via intramuscular or intravenous routes under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Adhere to sterile techniques during administration to minimize infection risks.
Benefits Compared to Analogues:
Ferrolek solution offers superior bioavailability and efficacy compared to traditional iron supplements, leading to faster and more pronounced improvements in iron status and hemoglobin levels.
Suitable Patient Groups:
Ferrolek solution is safe for use in adults, including the elderly, and is not recommended for children unless specifically prescribed by a healthcare provider based on individual needs.
Storage and Shelf Life:
Store Ferrolek solution in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use the product beyond the stated shelf life.
Packaging Description:
Ferrolek solution is available in 2 ml ampoules containing 50 mg/ml of the active ingredient. Each package contains 5 ampoules for multiple doses.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness:
Ferrolek solution has undergone clinical trials to assess its efficacy in managing iron deficiency anemia. Notably, a study published in the Journal of Hematology & Transfusion Science revealed significant improvements in hemoglobin levels and iron stores in patients treated with Ferrolek compared to a placebo group.
Additional Information:
- Pharmacological Effects: Ferrolek solution functions by replenishing iron stores crucial for hemoglobin and red blood cell synthesis.
- Clinical Trials: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial featured in the International Journal of Hematology highlighted the tolerability and effectiveness of Ferrolek solution in enhancing iron parameters in individuals with iron deficiency anemia.