Description
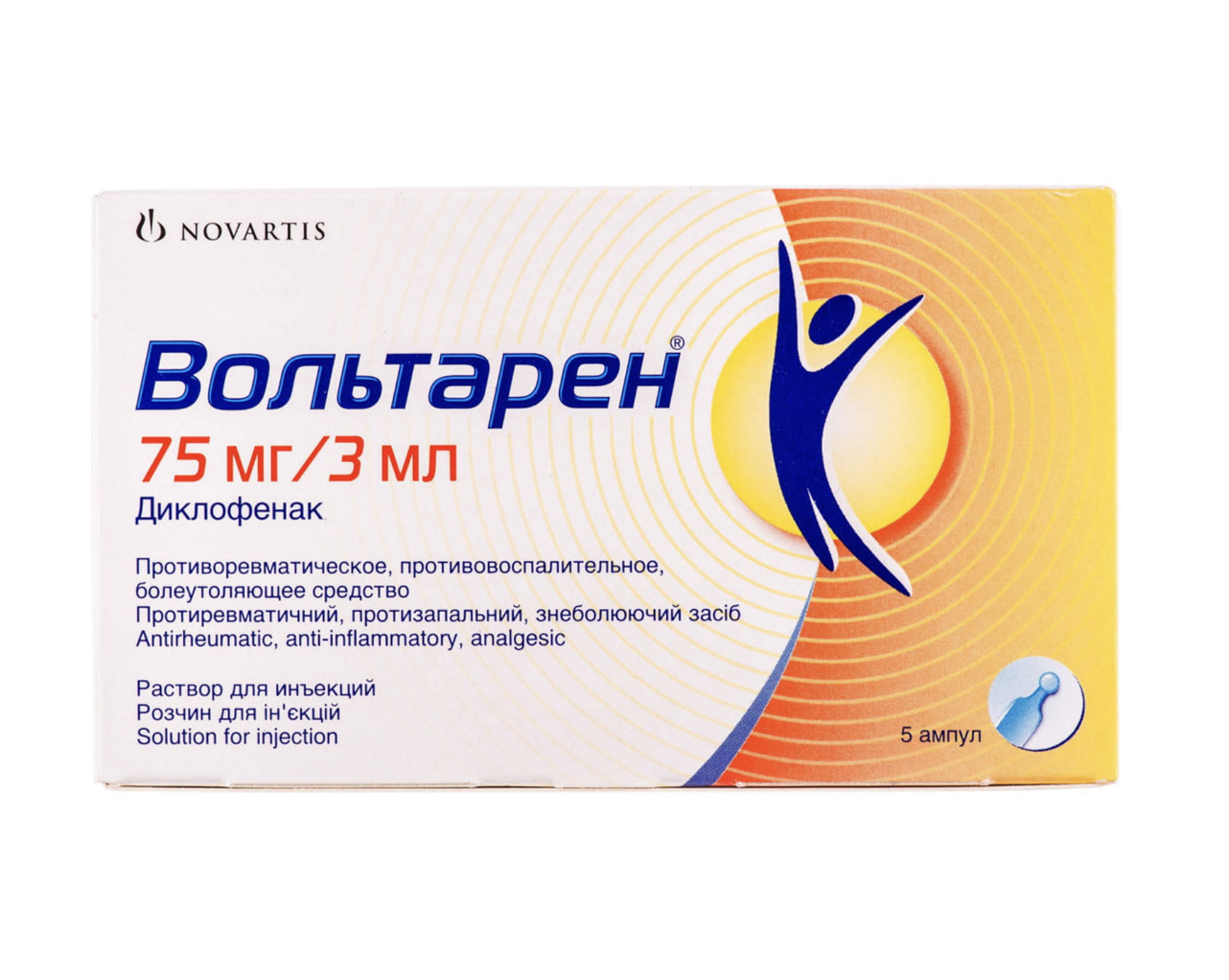
Voltaren (diclofenac sodium) Solution for Injection 75 mg. 3 ml Ampoules №5
Ingredients
- Active ingredient: diclofenac sodium
- Other ingredients: mannitol, water for injections
Dosage
Recommended dosage: The usual dose is 75 mg once daily, administered by deep intramuscular injection.
Indications
Voltaren solution for injection is indicated for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with musculoskeletal and joint disorders.
Contraindications
Do not use Voltaren solution for injection if you have a history of allergic reactions to diclofenac or other NSAIDs, or if you have a history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs.
Directions
Administer the injection deep into the muscle. Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment.
Scientific Evidence
Diclofenac sodium is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It works by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase, thereby reducing the production of prostaglandins which are involved in the inflammatory process.
Clinical trials have shown that diclofenac sodium is effective in managing pain and inflammation in various musculoskeletal conditions. A study published in the Journal of Pain Research demonstrated the superior efficacy of diclofenac compared to placebo in reducing pain intensity and improving function in patients with osteoarthritis.
Additional Information
- Storage: Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
- Caution: This medication should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal ulcers or bleeding disorders.