Description
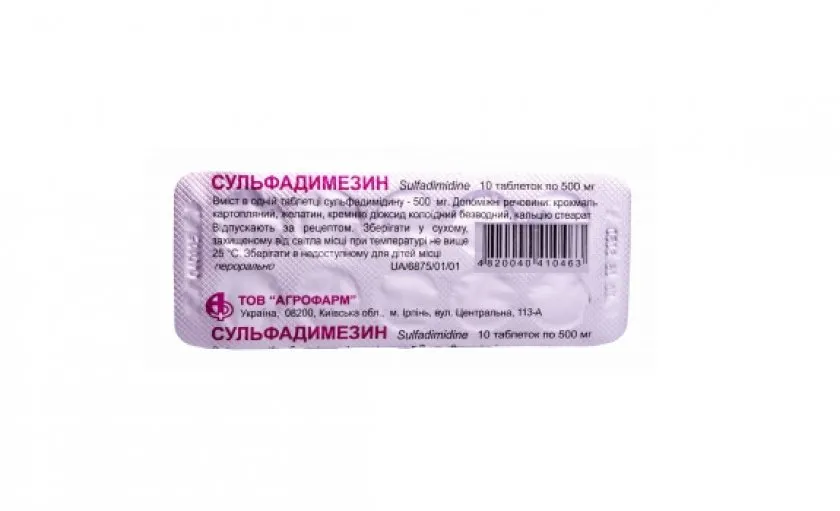
Sulfadimezin (sulfadimidine) Tablets 0.5 g. №10
Ingredients
- Active ingredient: Sulfadimidine 0.5 g per tablet.
Dosage
- Dosage: The usual adult dose is 1-2 tablets every 6 hours.
Indications
- Indications: Sulfadimezin tablets are indicated for the treatment of bacterial infections sensitive to sulfadimidine.
Contraindications
- Contraindications: Do not use in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to sulfonamides.
Directions
- Directions: Take the tablets orally with a full glass of water. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Scientific Evidence
Sulfadimezin (sulfadimidine) is a sulfonamide antibiotic with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, thereby preventing their growth and reproduction. Studies have shown the effectiveness of sulfadimidine in treating various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and wound infections.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of sulfadimidine in comparison to other antibiotics in the treatment of certain bacterial infections. Its ability to penetrate tissues and reach high concentrations at the site of infection makes it a valuable option in the management of susceptible bacterial diseases.