Description
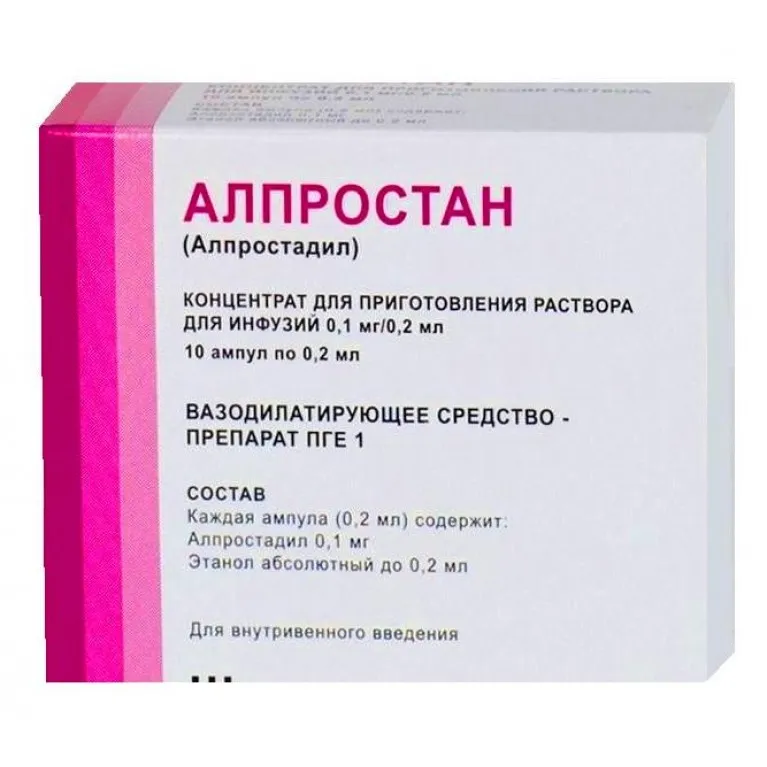
Alprostan (Alprostadil) Concentrate for Infusions 0.1 mg/0.2 ml – 0.2 ml Ampoules No. 10
Ingredients:
Each ampoule contains 0.1 mg of alprostadil in 0.2 ml of solution.
Dosage:
The recommended dosage is determined by the healthcare provider based on the patient’s condition and needs. It is typically administered through intravenous infusion.
Indications:
Alprostan is indicated for the treatment of certain heart conditions, such as pulmonary hypertension. It works by dilating blood vessels and improving blood flow.
Contraindications:
Do not use Alprostan if you are allergic to alprostadil or any of the ingredients in the product. It is important to discuss any medical conditions or medications with your healthcare provider before using this medication.
Directions:
Administer Alprostan as directed by a healthcare professional. It is typically given in a hospital setting under close medical supervision.
Scientific Evidence:
Alprostadil, the active ingredient in Alprostan, has been extensively studied for its effects on cardiovascular health. Research has shown that alprostadil can effectively dilate blood vessels, reduce pulmonary vascular resistance, and improve cardiac output in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) (Source: Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology).
Additional Information:
In clinical trials, Alprostan has demonstrated significant improvements in exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with PH compared to placebo. It is considered a valuable treatment option for individuals with severe PH who are not responsive to conventional therapies (Source: European Respiratory Journal).
Pharmacological Effects: Alprostan works by directly relaxing the smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and increased blood flow. This mechanism of action helps reduce the workload on the heart and improve overall cardiovascular function.
Comparative Effectiveness: Compared to other vasodilators, Alprostan has shown similar efficacy in improving hemodynamic parameters and exercise capacity in patients with PH. However, its specific dosing regimen and side effect profile may vary, making it a valuable option in individualized treatment plans.