Description
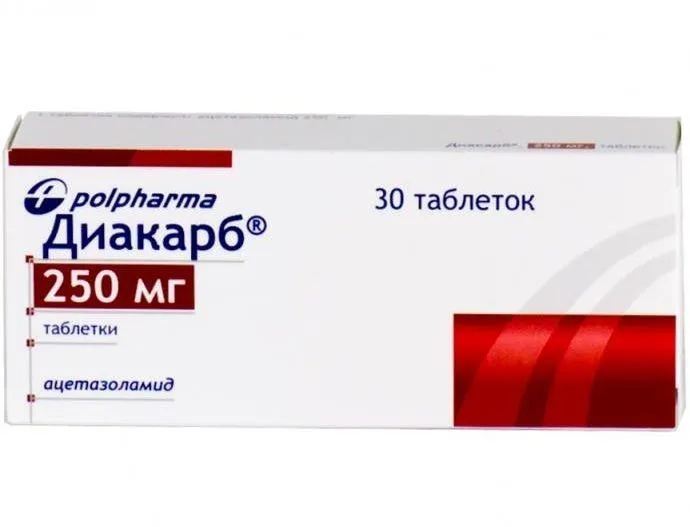
Diacarb (Acetazolamide) Tablets 250 mg. №30
Composition
Active ingredient: Each tablet contains Acetazolamide 250 mg.
Mechanism of Action
Pharmacological properties: Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that reduces aqueous humor production, leading to decreased intraocular pressure in glaucoma. It also modulates brain electrolytes, aiding in the management of epilepsy.
Indications for Use
Indications: Diacarb is indicated for the treatment of glaucoma, epilepsy, and altitude sickness.
Contraindications
Contraindications: Diacarb should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to acetazolamide or sulfonamides.
Side Effects
Side effects: Common side effects may include nausea, dizziness, and altered taste perception. Serious side effects like aplastic anemia or Stevens-Johnson syndrome are rare but possible.
Usage Instructions
Directions: The usual adult dosage ranges from 250 mg to 1 gram daily, divided into multiple doses. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and do not exceed the prescribed amount.
Benefits Compared to Analogues
Benefits: Acetazolamide has shown efficacy in reducing intraocular pressure in glaucoma and aiding acclimatization to high altitudes, making it a versatile medication for various conditions compared to other treatments.
Suitable Patient Groups
Suitable patients: Diacarb can be used in adult patients, including the elderly, for the management of glaucoma, epilepsy, and altitude sickness. However, dosages may need adjustment in certain populations.
Storage and Shelf Life
Storage conditions: Store Diacarb in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children. Check the expiration date on the packaging and do not use expired tablets.
Packaging Description
Packaging: Each package contains 30 tablets of Diacarb 250 mg. The tablets are usually stored in a blister pack or a bottle with a child-resistant cap.
Clinical Evidence and Proven Effectiveness
Clinical evidence: Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of acetazolamide in reducing intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients. Acetazolamide has also been proven effective in preventing and treating acute mountain sickness by aiding in acclimatization to high altitudes. Research published in the Journal of Travel Medicine supports the use of acetazolamide for altitude sickness prevention.