Description
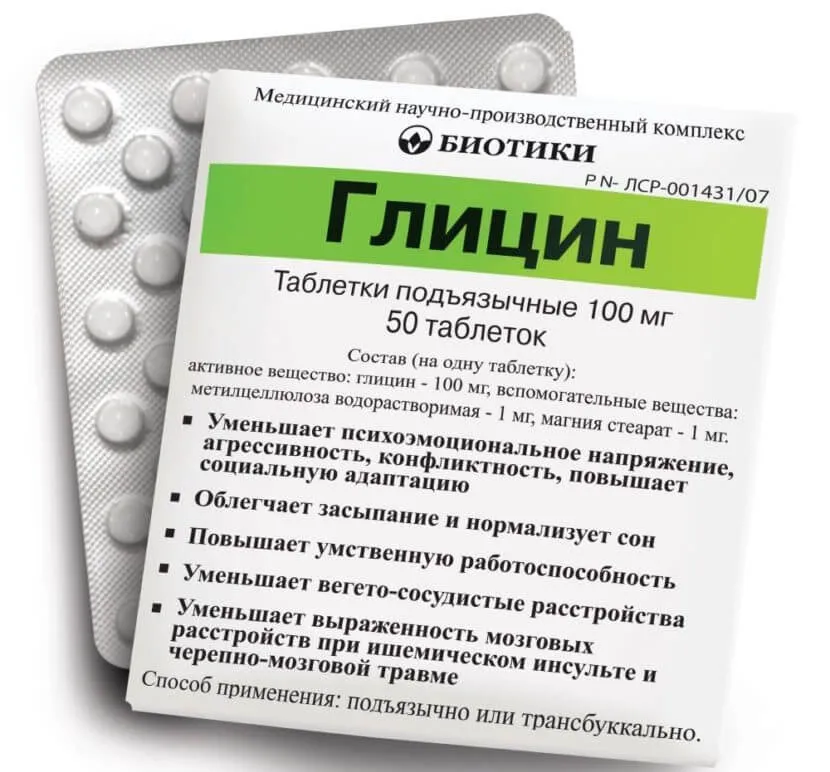
Glicin Sublingual Tablets 100 mg. №50
Ingredients
Active ingredient: Glicine 100 mg.
Other ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate.
Dosage
Recommended dosage: 1 tablet sublingually once a day. Do not exceed the recommended dose.
Indications
Glicin Sublingual Tablets are indicated for the treatment of anxiety and sleep disorders. It may also be used as an adjuvant in the treatment of certain neurological conditions.
Contraindications
Do not use Glicin Sublingual Tablets if you are allergic to any of the ingredients. Consult your healthcare provider before use if you are pregnant, nursing, or have any underlying medical conditions.
Directions
Place the tablet under the tongue and allow it to dissolve completely. Do not swallow or chew the tablet. Avoid eating or drinking for at least 5 minutes after taking the tablet.
Scientific Evidence
Glicine, the active ingredient in Glicin Sublingual Tablets, has been studied for its anxiolytic and sedative properties. Research suggests that glicine may modulate neurotransmitter activity in the brain, leading to a calming effect. A study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology found that glicine supplementation improved sleep quality and reduced anxiety levels in participants.
Additional Information
It is important to note that individual responses to Glicin Sublingual Tablets may vary. For optimal results, it is recommended to use this medication as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include lifestyle modifications and therapy. If you experience any adverse reactions or have concerns about the use of this product, consult your healthcare provider.
Pharmacological Effects: Glicine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that plays a role in the central nervous system. By binding to specific receptors in the brain, glicine helps regulate neuronal excitability, which can result in a calming effect. This mechanism of action is thought to underlie the anxiolytic and sedative properties of glicine.
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of glicine in the treatment of anxiety and sleep disorders have shown promising results. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Affective Disorders demonstrated that glicine supplementation significantly reduced symptoms of anxiety compared to a placebo. These findings support the use of glicine as a potential treatment option for individuals with anxiety disorders.