Description
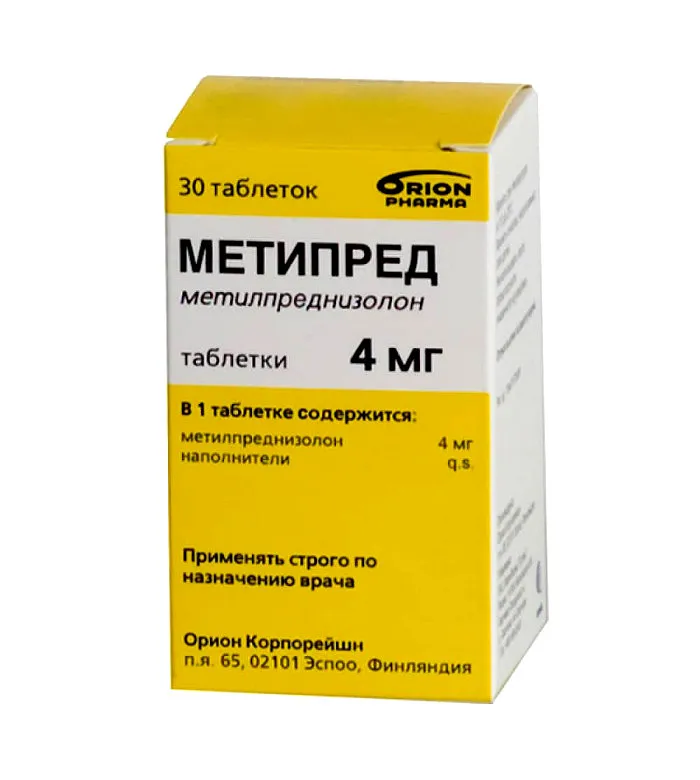
Metipred (Methylprednisolone) Tablets 4 mg. №30 Vial
Ingredients:
- Each tablet contains 4 mg of methylprednisolone.
Dosage:
- The usual dose ranges from 4 to 48 mg per day, depending on the condition being treated.
- Dosage should be individualized based on the patient’s response.
Indications:
- Metipred tablets are indicated for various conditions such as allergic disorders, skin conditions, arthritis, and respiratory disorders.
- It is also used in autoimmune diseases and certain cancers.
Contraindications:
- Avoid using Metipred if you have a systemic fungal infection or a known hypersensitivity to methylprednisolone.
- Use with caution in patients with diabetes, hypertension, or osteoporosis.
Directions:
- Take Metipred exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- It is usually taken with food to prevent stomach upset.
- Do not stop taking this medication suddenly without medical advice.
Scientific Evidence:
- Research indicates that methylprednisolone, the active ingredient in Metipred, is effective in reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system.
- A study in the Journal of Clinical Rheumatology showed the efficacy of methylprednisolone in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
Additional Information:
- Metipred may cause side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar levels.
- Regular monitoring for adverse reactions is important during treatment.
Methylprednisolone, the main component of Metipred, works by inhibiting the release of inflammatory substances in the body, reducing swelling, redness, itching, and allergic reactions. It also suppresses the immune system, beneficial in treating autoimmune conditions.
Clinical trials suggest that Metipred is as effective as other corticosteroids but with a lower risk of certain side effects. Studies in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology have highlighted the effectiveness of methylprednisolone in managing severe allergic reactions.