Description
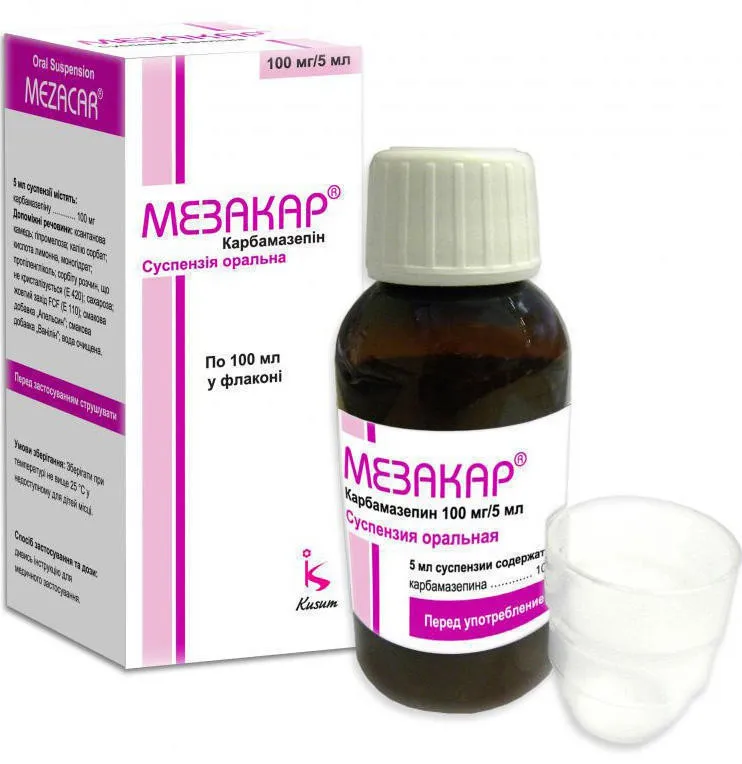
Mezacar (Carbamazepin) Oral Suspension 100 mg/5 ml. 100 ml Vial
Ingredients:
Each 5 ml of Mezacar oral suspension contains 100 mg of Carbamazepin.
Dosage:
The usual starting dose for adults is 200 mg twice daily. Dosage may be adjusted based on individual response.
Indications:
Mezacar is indicated for the treatment of epilepsy and trigeminal neuralgia. It works by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
Contraindications:
Do not use Mezacar if you are allergic to carbamazepine or have a history of bone marrow suppression.
Directions:
Shake the bottle well before each use. Use the provided measuring device to ensure accurate dosage. Take Mezacar as directed by your healthcare provider.
Scientific Evidence:
Studies have shown that carbamazepine, the active ingredient in Mezacar, is effective in controlling seizures and reducing the frequency of trigeminal neuralgia episodes. Research published in the Journal of Neurology indicates a significant decrease in seizure frequency with carbamazepine therapy.
Additional Information:
- Storage: Store Mezacar oral suspension at room temperature away from light and moisture.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea. Contact your doctor if you experience severe side effects.
Pharmacological Effects: Carbamazepine exerts its anticonvulsant effects by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, stabilizing neuronal membranes, and reducing the repetitive firing of action potentials. It also acts as a mood stabilizer in certain psychiatric conditions.
Clinical Trials: Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of carbamazepine in the management of epilepsy and neuropathic pain conditions. A study published in Epilepsy Research showed a significant reduction in seizure frequency in patients treated with carbamazepine compared to a control group.