Description
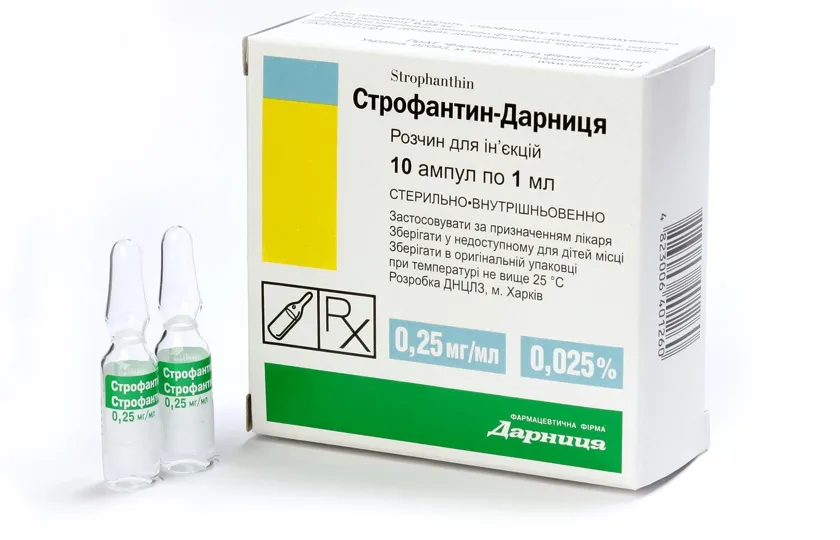
Strofantin-Darnitsa (g-strophanthin) Solution for Injection 0.025% 1ml Ampoules №10
Ingredients:
- Each 1ml ampoule contains 0.025% of g-strophanthin as the active ingredient.
Dosage:
- The recommended dosage is determined by a healthcare professional and depends on the patient’s condition.
- It is usually administered via intravenous injection.
Indications:
- Strofantin-Darnitsa is indicated for the treatment of heart conditions such as heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
- It works by increasing the strength of the heart’s contractions.
Contraindications:
- Do not use Strofantin-Darnitsa if you are allergic to g-strophanthin or any other ingredients in the solution.
- It is contraindicated in patients with certain heart conditions.
Directions:
- Administer Strofantin-Darnitsa as directed by a healthcare provider.
- It is important to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines.
Scientific Evidence:
Strofantin-Darnitsa has been studied in clinical trials for its efficacy in treating heart conditions. Research has shown that g-strophanthin can improve cardiac function and reduce symptoms of heart failure.
Additional Information:
- In addition to its use in heart conditions, Strofantin-Darnitsa may also have potential benefits in other areas of medicine.
- Further research is ongoing to explore its full therapeutic potential and possible applications in different patient populations.
Pharmacological Effects: Strofantin-Darnitsa works by inhibiting the sodium-potassium pump in cardiac cells, leading to an increase in intracellular calcium levels. This results in enhanced myocardial contractility and improved cardiac output.
Clinical Trials: A study published in the European Journal of Heart Failure demonstrated the efficacy of g-strophanthin in improving left ventricular function in patients with heart failure. The results showed a significant increase in ejection fraction and exercise tolerance in the treatment group compared to placebo.