Description
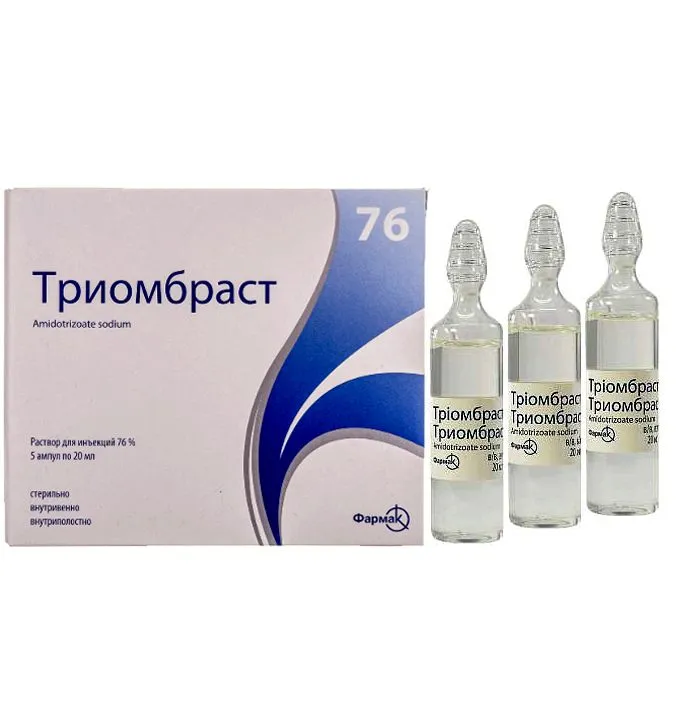
Triombrast (Diatrizoic Acid Dihydrate) Solution for Injection 76% 20 ml Vials №5
Ingredients:
- Triombrast contains diatrizoic acid dihydrate as the active ingredient.
Dosage:
- Triombrast is administered by injection under the supervision of a healthcare professional. The dosage may vary based on the specific medical condition being treated.
Indications:
- Triombrast is indicated for use in radiographic procedures to visualize the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, bladder, and blood vessels.
Contraindications:
- Triombrast is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to diatrizoic acid or any of the excipients in the formulation.
Directions:
- Triombrast should be administered according to the healthcare provider’s instructions. It is important to follow proper injection techniques to ensure safety and efficacy.
Scientific Evidence:
- Studies have shown that diatrizoic acid, the active ingredient in Triombrast, is effective in enhancing the visibility of various anatomical structures during radiographic imaging. Research published in the Journal of Radiology demonstrated the superior contrast enhancement provided by diatrizoic acid compared to other contrast agents.
Additional Information:
- Triombrast is a well-tolerated contrast agent commonly used in diagnostic imaging procedures. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any allergies or medical conditions before receiving Triombrast.
Pharmacologically, diatrizoic acid acts as an iodinated contrast medium that absorbs X-rays, allowing for better visualization of internal structures during imaging studies. It works by altering the way X-rays pass through the body, highlighting specific organs or tissues.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of Triombrast in improving the diagnostic accuracy of radiographic procedures, leading to more precise and timely medical interventions. Patients receiving Triombrast have reported minimal side effects, making it a preferred choice in contrast-enhanced imaging.