Description
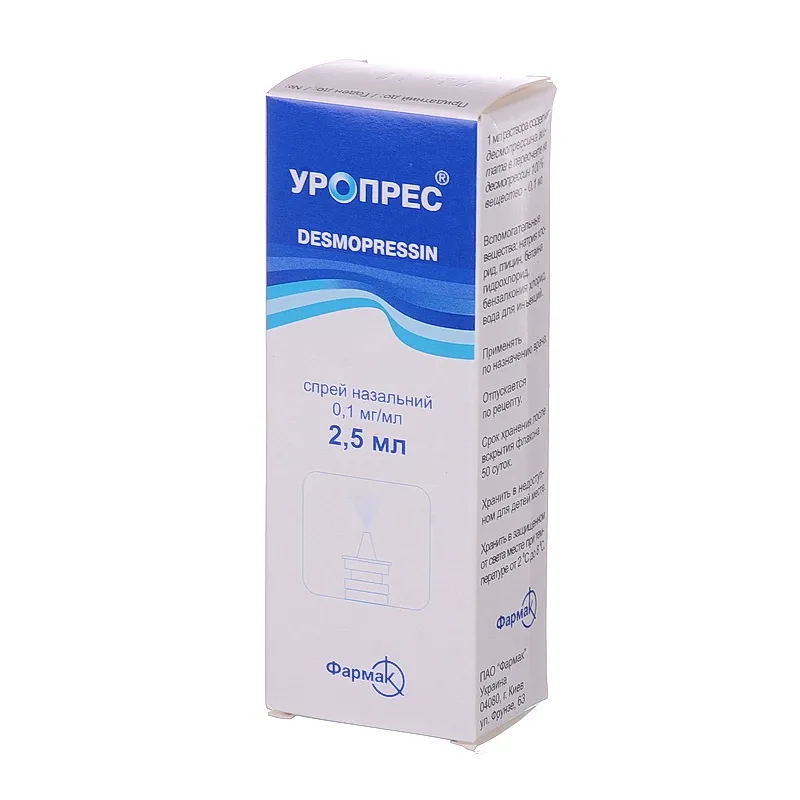
Uropres (Desmopressin) Nasal Spray 0.1 mg/ml – 2.5 ml Vial
Ingredients
- Desmopressin acetate is the active ingredient in Uropres nasal spray.
- Other ingredients include benzalkonium chloride, sodium chloride, and hydrochloric acid.
Dosage
The recommended dosage for Uropres nasal spray is usually 1 spray (0.1 mg) into one nostril daily. Follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Indications
Uropres nasal spray is indicated for the treatment of central diabetes insipidus, nocturnal enuresis, and for managing excessive thirst and urination.
Contraindications
Do not use Uropres nasal spray if you are allergic to desmopressin or any other ingredients in the product. Inform your healthcare provider about any medical conditions or medications before use.
Directions
Before using Uropres nasal spray, gently blow your nose to clear the nasal passages. Insert the tip of the spray into one nostril and press down on the pump to release the medication. Repeat for the other nostril if instructed.
Scientific Evidence
- Studies have shown that desmopressin effectively reduces urine production and increases urine concentration in patients with diabetes insipidus.
- Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in managing nocturnal enuresis in both children and adults.
Additional Information
- Store Uropres nasal spray at room temperature away from light and moisture.
- Keep the vial tightly closed when not in use.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it is almost time for your next dose.
Desmopressin acts by mimicking the action of vasopressin, a hormone that regulates water balance in the body. It reduces urine production, leading to decreased urination frequency and increased urine concentration.
Clinical trials have compared desmopressin nasal spray with other formulations, showing similar efficacy in managing conditions like diabetes insipidus and nocturnal enuresis. The nasal spray offers a convenient and non-invasive administration route for patients.