Description
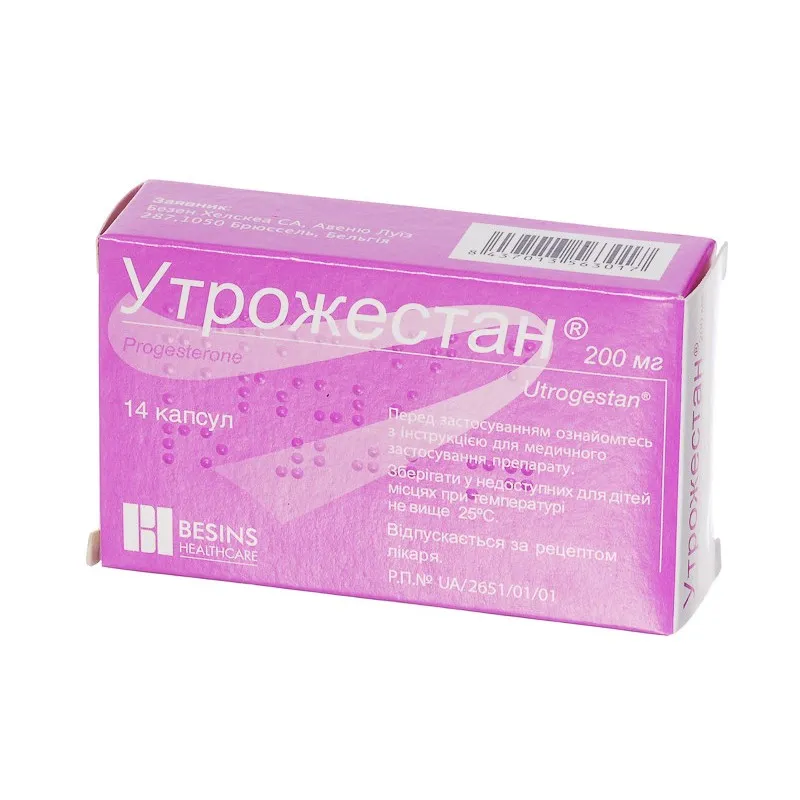
Utrojestan (Progesterone) Capsules 200 mg. №14
Ingredients
Active ingredient: Progesterone 200 mg.
Other ingredients: Maize starch, colloidal silica anhydrous, magnesium stearate.
Dosage
Adult dosage: The usual dose is one capsule daily, preferably taken at bedtime.
Indications
Utrojestan capsules are indicated for:
- Progesterone deficiency
- Assisted reproduction techniques
- Menstrual disorders
Contraindications
Do not use Utrojestan capsules if you have:
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Active thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Severe hepatic dysfunction
Directions
Swallow the capsule whole with a glass of water. Do not chew the capsule. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Scientific Evidence
Progesterone, the active ingredient in Utrojestan capsules, plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Studies have shown that progesterone supplementation can help support early pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
Additional Information
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully when using Utrojestan capsules. If you experience any unusual symptoms or side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Keep this medication out of reach of children and store it at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Progesterone is a hormone that is naturally produced by the body and is essential for maintaining pregnancy. Utrojestan capsules provide progesterone supplementation when the body is not producing enough on its own. Clinical trials have shown that progesterone therapy can be effective in supporting pregnancy and reducing the risk of preterm birth in certain high-risk populations.