Description
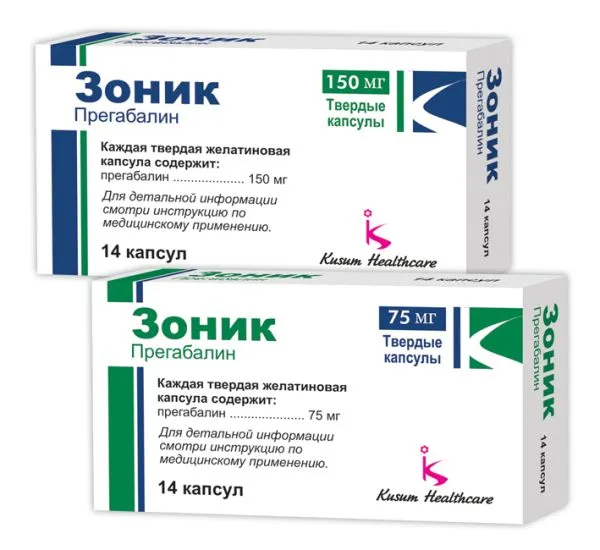
Zonik (Pregabalin) 75 mg Hard Capsules
Ingredients:
Each hard capsule contains 75 mg of pregabalin.
Dosage:
The typical dose of Zonik (pregabalin) is 75 mg taken orally twice daily. Dosage may be adjusted based on individual response and medical condition.
Indications:
Zonik (pregabalin) is used to manage neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia.
Contraindications:
Avoid using Zonik (pregabalin) if you have a known allergy to pregabalin or any other capsule ingredients.
Directions:
Take Zonik (pregabalin) as directed by your healthcare provider. Swallow the capsules whole with water; do not crush or chew them.
Mechanism of Action:
Pregabalin, the active component in Zonik, works by binding to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. This action reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, thereby modulating pain signaling pathways.
Scientific Evidence:
Clinical trials have shown the efficacy of pregabalin in treating neuropathic pain conditions. Research by Rosenstock et al. (2004) demonstrated significant pain relief in diabetic neuropathy patients treated with pregabalin compared to a placebo.
Additional Information:
- Pregabalin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Avoid driving or operating machinery until you understand how this medication affects you.
- Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Zonik (pregabalin).