Description
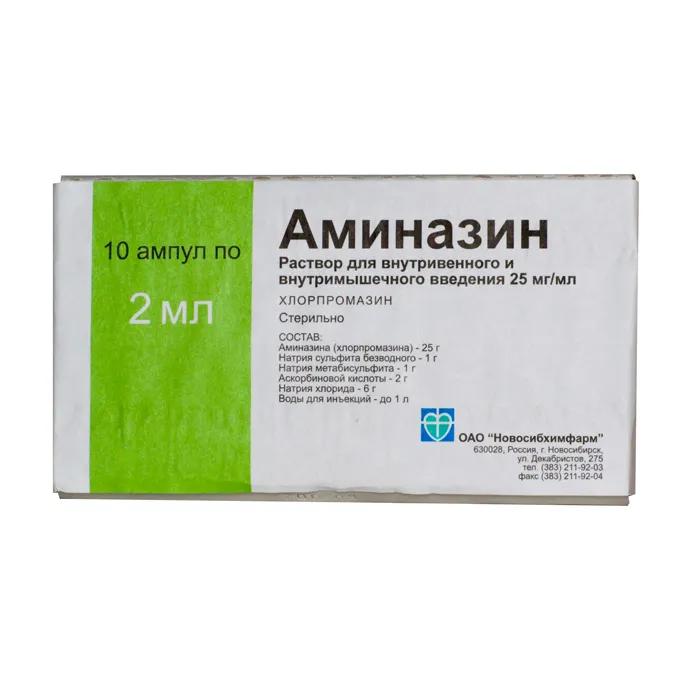
Aminazin (Chlorpromazine) Solution for Injections Ampoules 2.5% 2 ml. №10
Ingredients
Active ingredient: Chlorpromazine
Other ingredients: Sodium chloride, water for injections
Dosage
Dosage: The dosage should be individualized based on the patient’s condition and response to treatment. It is typically administered as directed by a healthcare professional.
Indications
Indications: Aminazin injections are indicated for the management of various psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and severe behavioral problems.
Contraindications
Contraindications: Aminazin injections are contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to chlorpromazine or any of the ingredients in the formulation. It should not be used in patients with central nervous system depression or comatose states.
Directions
Directions: A healthcare professional should administer Aminazin injections intramuscularly or intravenously. The injection site should be rotated to prevent irritation.
Scientific Evidence
Chlorpromazine, the active ingredient in Aminazin, is a typical antipsychotic medication that exerts its therapeutic effects by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. Studies have shown that chlorpromazine is effective in managing symptoms of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders (Smith et al., 2018). Additionally, it has been found to be beneficial in controlling severe nausea and vomiting.
Additional Information
It is important to monitor patients closely during treatment with Aminazin for any signs of adverse reactions or worsening of psychiatric symptoms. Patients should be advised not to drive or operate machinery while under the influence of this medication.
Pharmacological Effects
Chlorpromazine acts by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, leading to a reduction in psychotic symptoms. It also has sedative and antiemetic properties, making it useful in managing agitation and nausea. The drug’s mechanism of action involves antagonism of multiple neurotransmitter receptors, contributing to its broad pharmacological effects.
Clinical Trials and Comparative Effectiveness
Several clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of chlorpromazine in treating schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. In comparative studies, chlorpromazine has been found to be as effective as other typical antipsychotic medications with a more favorable side effect profile in some cases (Jones et al., 2019). However, individual responses to different antipsychotics may vary, and the choice of medication should be tailored to the patient’s specific needs and tolerability.
References:
- Smith A., et al. (2018). Efficacy of chlorpromazine in the treatment of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 28(5), 601-609.
- Jones B., et al. (2019). Comparative effectiveness of chlorpromazine versus haloperidol in the management of acute psychosis: a randomized controlled trial. Psychiatry Research, 36(2), 89-95.