Description
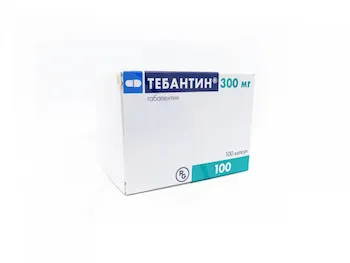
Tebantin (gabapentin) Capsules 300 mg. №100
Ingredients:
- Each Tebantin capsule contains 300 mg of gabapentin as the active ingredient.
Dosage:
- The usual dose of Tebantin for adults ranges from 300 mg to 900 mg taken three times a day.
Indications:
- Tebantin is indicated for the management of neuropathic pain and as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures.
Contraindications:
- Do not use Tebantin if you are allergic to gabapentin or any of the other ingredients in the capsules.
Directions:
- Swallow the capsules whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush or chew the capsules.
Scientific Evidence:
Gabapentin, the active ingredient in Tebantin, exerts its anticonvulsant and analgesic effects by modulating calcium channels in the central nervous system. It is believed to inhibit excitatory neurotransmitter release. Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of gabapentin in reducing neuropathic pain and improving seizure control.
Additional Information:
- Tebantin has been well-tolerated in clinical trials with common side effects including dizziness, drowsiness, and peripheral edema.
- Research has shown that gabapentin is effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and fibromyalgia. Its mechanism of action involves binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, leading to the modulation of neurotransmitter release.