Description
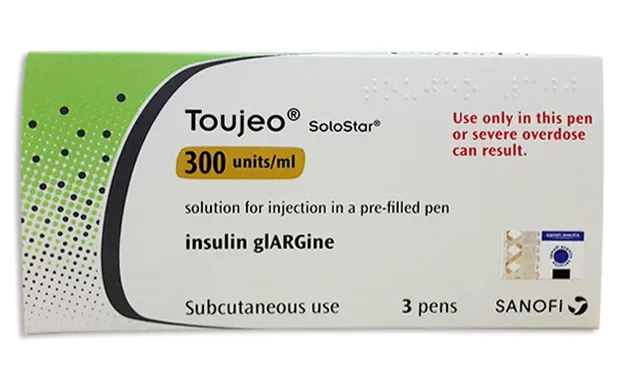
Tojeo SoloStar (Insulin Glargine) Solution for Injections 300 IU/ml. 1.5 ml. №3 Cart. Syringe
Ingredients:
- Tojeo SoloStar contains insulin glargine as the active ingredient.
- Other ingredients include glycerol, metacresol, zinc oxide, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide.
Dosage:
Tojeo SoloStar is administered subcutaneously once daily at the same time each day. The dosage may vary depending on the individual’s needs and should be determined by a healthcare provider.
Indications:
Tojeo SoloStar is indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults. It helps control blood sugar levels and is essential for managing diabetes effectively.
Contraindications:
Tojeo SoloStar is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to insulin glargine or any other components of the solution. It should not be used during episodes of hypoglycemia.
Directions:
- Before each use, inspect the solution visually for any particles or discoloration.
- Administer the injection subcutaneously into the thigh, abdomen, or upper arm.
- Rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy.
Scientific Evidence:
Studies have shown that Tojeo SoloStar provides effective glycemic control in patients with diabetes. Research published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology demonstrated the long-acting and stable glucose-lowering effects of insulin glargine.
Additional Information:
- It is important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly while using Tojeo SoloStar to adjust the dosage as needed.
- Tojeo SoloStar works by mimicking the natural insulin produced by the body, helping to regulate glucose levels in the blood.
- Compared to other insulin formulations, Tojeo SoloStar offers the advantage of once-daily dosing, reducing the frequency of injections for patients with diabetes.
- Clinical trials have shown its efficacy in improving glycemic control and reducing the risk of hypoglycemia.