Description
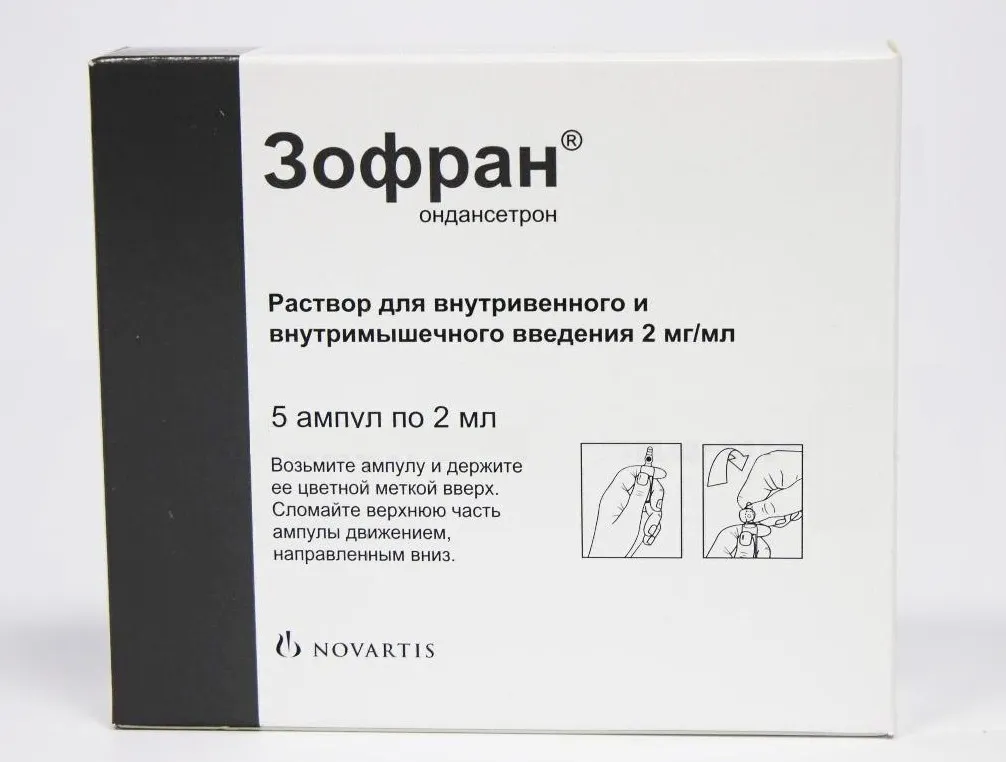
Zofran (Ondansetron) Solution for Injections Ampoules 2 mg/ml. 2 ml. №5
Ingredients:
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 4 mg of ondansetron (as hydrochloride dihydrate) as the active ingredient. Other ingredients include citric acid, sodium chloride, and water for injections.
Dosage:
The usual adult dose is 8 mg administered by slow intravenous injection or infusion immediately before chemotherapy, followed by 8 mg orally 12 hours later. Dosage adjustments may be needed based on individual patient characteristics.
Indications:
Zofran injections are indicated for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. It is also used for the prevention and treatment of post-operative nausea and vomiting.
Contraindications:
Do not use Zofran if you are allergic to ondansetron or any other ingredients in the formulation. It is contraindicated in patients taking apomorphine.
Directions:
Administer Zofran as directed by a healthcare professional. The solution should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration before administration.
Scientific Evidence:
Ondansetron, the active ingredient in Zofran, is a selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist that works by blocking serotonin both peripherally on vagal nerve terminals and centrally in the chemoreceptor trigger zone. This mechanism effectively reduces nausea and vomiting.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of ondansetron in preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that ondansetron was significantly more effective than traditional antiemetics in controlling emesis in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Additional Information:
- Storage: Store Zofran injections at controlled room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include headache, constipation, and fatigue.